Glossarbegriffe: Sonne
Description: Die Sonne ist der Stern, der der Erde am nächsten ist. Für die Astronomen ist sie ein Stern des Typs "G2V". Das bedeutet: Die Sonne ist ein Hauptreihenstern mit einer typischen Temperatur ("effektive Temperatur") von 5800 Kelvin. Hauptreihensterne wie die Sonne sind stabil, man sagt auch: Sie befinden sich im hydrostatischen Gleichgewicht. Das bedeutet, dass die durch Wasserstofffusion in ihrem Kern freigesetzte Energie die durch die Schwerkraft nach innen gerichtete Kraft ausgleicht.
Dem menschliche Auge erscheint die Sonne weiß, da sie viel Licht im gesamten sichtbaren Spektrum aussendet. Wenn sie tiefer am Himmel steht, kann die erhöhte atmosphärische Extinktion die Sonne gelb oder orange erscheinen lassen, weshalb sie häufig als gelb dargestellt wird. Es gibt Sterne, die mehr als 1000-mal heller sind als die Sonne, aber auch solche, die 1000-mal lichtschwächer sind. Viel hellere Sterne sind jedoch relativ selten: Die Sonne ist heller (und massereicher) als die meisten (vielleicht 85 %) der Sterne in der Galaxis.
Für Astronomen ist die Sonne interessant, weil sie so nah ist: Deshalb können sie ihre Oberfläche detaillierter auflösen und so die Strukturen und Phänomene auf der Sonne untersuchen. Ein Beispiel ist die Sonnenaktivität, die mit den Magnetfeldern der Sonne zusammenhängt: Sonnenflecken (kühlere Bereiche), Flares (kurze helle Sonneneruptionen) und sogar koronale Massenauswürfe (elektrisch geladene Teilchen, die von der Sonne weggeschleudert werden). Physiker haben auch Elementarteilchen, sogenannte Neutrinos, aus dem Kern der Sonne nachgewiesen: Die Neutrinos sind ein direkter Beweis für Kernfusionsprozesse tief im Inneren der Sonne. Das Element Helium wurde erstmals im Sonnenspektrum nachgewiesen - daher der Name Helium, der von Helios (in der griechischen Mythologie der Sonnengott) stammt.
Zugehörige Glossarbegriffe:
- Hauptreihe
- Kernfusion
- Sonneneruption
- Stern
- Sonnenfleck
- Effektivtemperatur
- Magnetfeld
- Neutrino
- Koronaler Massenauswurf (CME)
See this term in other languages
Term and definition status: The original definition of this term in English have been approved by a research astronomer and a teacher The translation of this term and its definition is still awaiting approval
The OAE Multilingual Glossary is a project of the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education (OAE) in collaboration with the IAU Office of Astronomy Outreach (OAO). The terms and definitions were chosen, written and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits here. All glossary terms and their definitions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE".
Zugehörige Medien
Winter Haloes, by Thomas Gigl, Germany
Bildnachweis: Thomas Gigl/IAU OAE
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Namensnennung 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Sunspots
Bildnachweis: NASA/SDO/HMI credit link
License: PD Public Domain icons
Solar flare
Bildnachweis: NASA/SDO credit link
License: PD Public Domain icons
Related Activities
Measure the Solar Diameter
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Hands-on activity to measure the Sun by using household materials.License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Namensnennung 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags: Hands-on , Scales , Observing , Measurement Age Ranges: 12-14 , 14-16 , 16-19 , 19+ Education Level: Middle School Areas of Learning: Social Research Costs: Low Cost Group Size: Group Skills: Communicating information , Constructing explanations , Using mathematics and computational thinkingCounting Sunspots
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Counting the Sunspots using real solar images and data.License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Namensnennung 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags: Hands-on , Sunspots , Data analysis Age Ranges: 16-19 Areas of Learning: Observation based Costs: Low Cost Duration: 1 hour Group Size: Group Skills: Analysing and interpreting data , Constructing explanations , Using mathematics and computational thinkingMeet Our Neighbours: Sun
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Explore the tactile version of our star; the Sun with household materials.License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Namensnennung 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags: Hands-on , Model , Sunspots , Visually Impaired , Tactile Age Ranges: 6-8 , 8-10 , 10-12 Education Level: Middle School , Primary , Secondary Areas of Learning: Interactive Lecture , Modelling Costs: Low Cost Duration: 1 hour Group Size: Group Skills: Analysing and interpreting data , Developing and using modelsBuild a Safe Sun Viewer
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Build a safe Sun viewer using cheap household items and learn why it is dangerous to look directly at the Sun, even briefly.License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Namensnennung 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags: Hands-on , Safety Age Ranges: 6-8 , 8-10 , 10-12 Education Level: Primary , Secondary Areas of Learning: Modelling , Observation based Costs: Low Cost Group Size: Group Skills: Planning and carrying out investigationsSolar System Model
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Make a model of the Solar System planets using household materials.License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Namensnennung 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags: Hands-on , Model , Planets Age Ranges: 4-6 , 6-8 , 8-10 Education Level: Pre-school , Primary Areas of Learning: Modelling Costs: Low Cost Duration: 30 mins Group Size: Group Skills: Analysing and interpreting data , Asking questions , Communicating information , Developing and using modelsSun’s Shadow
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Why is the Sun's shadow so important?License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Namensnennung 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags: Hands-on , Shadows Age Ranges: 6-8 , 8-10 , 10-12 , 12-14 , 14-16 Education Level: Informal , Middle School , Primary , Secondary Areas of Learning: Observation based , Social Research Costs: Medium Cost Duration: 1 day Group Size: Group Skills: Asking questions , Communicating information , Constructing explanations , Engaging in argument from evidenceSun, Earth and Moon Model
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Build an Earth-Moon-Sun mobile to learn about how they orbit.License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Namensnennung 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags: Hands-on , Model Age Ranges: 8-10 Education Level: Primary Areas of Learning: Game-mediated learning , Modelling , Social Research Costs: Medium Cost Duration: 1 hour 30 mins Group Size: Group Skills: Asking questions , Communicating information , Developing and using modelsKnow Your Planets
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Play a game of card and learn about the Sun and planets.License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Namensnennung 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags: Game , Planets Age Ranges: 4-6 , 6-8 , 8-10 Education Level: Pre-school , Primary Areas of Learning: Game-mediated learning , Social Research Costs: Low Cost Duration: 1 hour Group Size: Group Skills: Analysing and interpreting data , Asking questions , Communicating informationSeasons Around the World
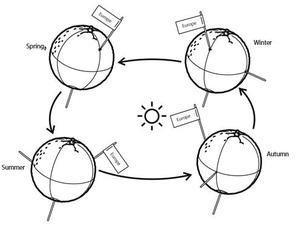
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Demonstrate the seasons on Earth using a model.License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Namensnennung 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags: Hands-on , Model Age Ranges: 6-8 , 8-10 , 10-12 Education Level: Middle School , Primary Areas of Learning: Modelling , Social Research Costs: Medium Cost Duration: 45 mins Group Size: Group Skills: Analysing and interpreting data , Asking questions , Constructing explanations , Developing and using models , Planning and carrying out investigationsNavigate like a Viking – Use the Sun, not your phone!
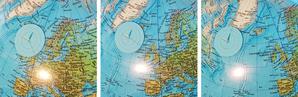
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Learn how the Vikings used the sky to navigate at sea with a hands-on activity!License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Namensnennung 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags: History , Geography , Maps , Coordinates , Celestial navigation Age Ranges: 12-14 , 14-16 Education Level: Middle School Areas of Learning: Discussion Groups , Modelling , Social Research Costs: Medium Cost Duration: 1 hour 30 mins Group Size: Group Skills: Analysing and interpreting data , Asking questions , Communicating information , Developing and using models , Planning and carrying out investigations , Using mathematics and computational thinkingMeasure the Sun's Rotation Period
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Find out the Sun’s rotation period, applying the simple equation of average speed to a real astronomical case.License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Namensnennung 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags: Hands-on , History , Experiment , Galileo , average speed Age Ranges: 16-19 Education Level: Secondary Areas of Learning: Social Research Costs: Low Cost Duration: 1 hour 30 mins Group Size: Group Skills: Analysing and interpreting data , Engaging in argument from evidence , Planning and carrying out investigations , Using mathematics and computational thinkingOne Million Earths inside our Sun
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Learn how to build a model of the Sun...which can fit nearly 1 million little Earth balls!License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Namensnennung 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags: Hands-on , Model , Scales , Distances , Dimension , Relative sizes Age Ranges: 4-6 , 6-8 , 8-10 , 10-12 , 12-14 , 14-16 , 16-19 , 19+ Education Level: Informal , Middle School , Other , Pre-school , Primary , Secondary , University Areas of Learning: Guided-discovery learning , Modelling , Problem-solving Costs: Medium Cost Duration: 30 mins Group Size: Group Skills: Analysing and interpreting data , Asking questions , Communicating information , Developing and using models , Using mathematics and computational thinkingIs the Sun rotating? Follow the sunspots!
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Like a "modern" Galileo, use true astronomical satellite observations to discover if the Sun (and other celestial objects) are rotating!License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Namensnennung 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags: Hands-on , History , Experiment , Galileo Age Ranges: 12-14 , 14-16 , 16-19 Education Level: Middle School , Secondary Areas of Learning: Social Research Costs: Low Cost Duration: 1 hour Group Size: Group Skills: Analysing and interpreting data , Planning and carrying out investigationsMake your own Sun!
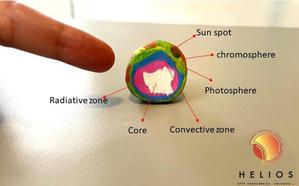
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Let's build a model of the Sun with plasticine and get to know our star!License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Namensnennung 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags: Hands-on , Model , Sun model , Galileo teachers Age Ranges: 6-8 , 8-10 , 10-12 Education Level: Primary Areas of Learning: Guided-discovery learning , Modelling Costs: Low Cost Duration: 1 hour 30 mins Group Size: Group Skills: Asking questions , Communicating information , Developing and using modelsThe Sun in our box
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Comparing the size of the Sun and the Earth building and using a pinhole camera.License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Namensnennung 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Age Ranges: 10-12 , 12-14 Education Level: Middle School Areas of Learning: Discussion Groups , Observation based , Project-based learning , Social Research Costs: Low Cost Duration: 3 hours Group Size: Group Skills: Developing and using models , Engaging in argument from evidence , Using mathematics and computational thinking