Glossarbegriffe: B-Stern
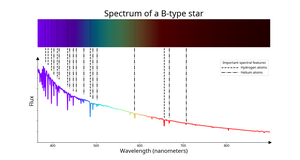
Description: Ein Stern mit dem Spektraltyp "B". Astronomen erkennen Sterne der Spektralklasse B daran, dass in ihren Spektren neben Wasserstofflinien auch neutrale Heliumlinien zu finden sind. Sie haben typische (effektive) Temperaturen zwischen etwa 10.000 Kelvin (K) und 30.000 K. Im Vergleich zu anderen Sternen erscheinen sie dem menschlichen Auge bläulich-weiß, es sei denn, die interstellare oder atmosphärische Extinktion spielt eine Rolle, wodurch das Licht eines Sterns röter erscheint als es wirklich ist. Beispiele für B-Sterne sind Regulus im Löwen, Rigel im Orion und Spica in der Jungfrau.
Zugehörige Glossarbegriffe:
See this term in other languages
Term and definition status: The original definition of this term in English have been approved by a research astronomer and a teacher The translation of this term and its definition is still awaiting approval
The OAE Multilingual Glossary is a project of the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education (OAE) in collaboration with the IAU Office of Astronomy Outreach (OAO). The terms and definitions were chosen, written and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits here. All glossary terms and their definitions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE".
Related Diagrams
Spectrum of a B-type star
Bildnachweis: IAU OAE/SDSS/Niall Deacon
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Namensnennung 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons