Glossary term: Polaris
Description: Polaris est l'étoile brillante la plus proche (à un degré près) du pôle Nord céleste. Sa désignation officielle est α Ursae Minoris, mais elle est communément appelée Polaris, l'étoile polaire ou encore l'étoile du Nord. Toutes les étoiles de l'hémisphère nord semblent tourner autour d'elle, ce qui en fait un excellent point fixe à partir duquel on peut effectuer des mesures pour la navigation et l'astrométrie. Son élévation au-dessus de l'horizon donne la latitude approximative du site d'observation. Cependant, sa position sur la sphère céleste change lentement en raison de la précession de l'axe de rotation de la Terre, de sorte que dans plusieurs siècles, Polaris n'indiquera plus la position du pôle Nord céleste.
Polaris est un système stellaire triple, composé d'une étoile primaire, une supergéante jaune appelée Polaris Aa, en orbite avec un compagnon plus petit, Polaris Ab, une étoile de séquence principale très proche ; la paire a un compagnon plus éloigné, Polaris B, une étoile de séquence principale en orbite à une distance de 2400 unités astronomiques (la période orbitale est d'environ 29,3 ans). Polaris B peut être résolue avec un télescope modeste. Le télescope spatial Hubble a été capable de résoudre les trois membres du système ternaire de Polaris. La magnitude visuelle apparente de Polaris fluctue car Polaris Aa est une variable céphéide. Le système Polaris se trouve à environ 447 années-lumière de la Terre.
Term and definition status: The original definition of this term in English have been approved by a research astronomer and a teacher The translation of this term and its definition have been approved by a research astronomer and a teacher
The OAE Multilingual Glossary is a project of the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education (OAE) in collaboration with the IAU Office of Astronomy Outreach (OAO). The terms and definitions were chosen, written and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits here. All glossary terms and their definitions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE".
If you notice a factual or translation error in this glossary term or definition then please get in touch.
Related Media
Dreamlike Starry Sky and Airglow
Credit: Likai Lin/IAU OAE
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
La Grande Ourse aux quatre saisons
Credit: Giorgia Hofer/IAU OAE
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Big Dipper and Comet Neowise C2020 F3
Credit: Giorgia Hofer/IAU OAE (CC BY 4.0)
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
The Big Dipper with the Sardinia Radio Telescope SRT
Credit: Antonio Finazzi/IAU OAE (CC BY 4.0)
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Big Dipper Over the Mono Lake
Credit: Fabrizio Melandri/IAU OAE (CC BY 4.0)
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Related Diagrams
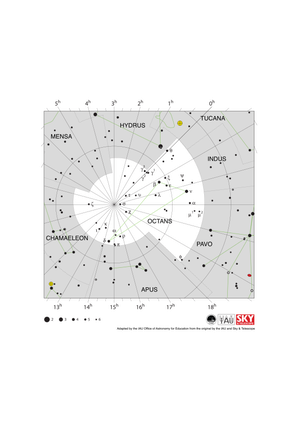
Octans Constellation Map
Credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by IAU/Sky & Telescope
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
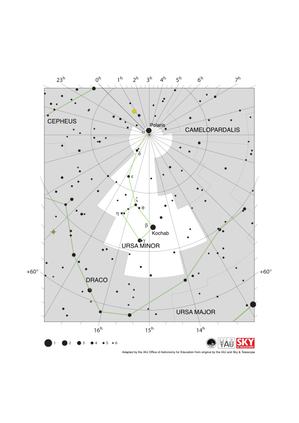
Ursa Minor Constellation Map
Credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by IAU/Sky & Telescope
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Related Activities
Navigating with the Kamal – Northern Hemisphere
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: How did Arabian sailors navigate at sea?
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
History
, Geography
, Coordinates
, Celestial navigation
, Arabia
, Kamal
Age Ranges:
14-16
, 16-19
Education Level:
Middle School
, Secondary
Areas of Learning:
Modelling
, Social Research
Costs:
Low Cost
Duration:
1 hour 30 mins
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Analysing and interpreting data
, Asking questions
, Communicating information
, Developing and using models
, Planning and carrying out investigations