Glossary term: कृत्रिम उपग्रह
Description: कृत्रिम उपग्रह एक मानव निर्मित उपकरण है जिसे पृथ्वी या अन्य सौर मंडल की वस्तुओं की परिक्रमा करने के लिए अंतरिक्ष में भेजा जाता है, जहां गुरुत्वाकर्षण इसे कक्षा में रखता है। कृत्रिम उपग्रहों को विभिन्न प्रकार के कार्यों को करने के लिए डिज़ाइन किया जा सकता है, जिसमें मौसम विज्ञानियों को मौसम की भविष्यवाणी करने में मदद करने के लिए पृथ्वी की हवाई तस्वीरें लेना, या खगोलीय पिंडों और दूर की आकाशगंगाओं की तस्वीरें लेना शामिल है, जिससे वैज्ञानिकों को ब्रह्मांडीय प्रणाली को बेहतर ढंग से समझने में मदद मिलती है। कृत्रिम उपग्रहों का उपयोग मुख्य रूप से विश्वव्यापी संचार और किसी के स्थान का पता लगाने के लिए भी किया जाता है, जैसे ग्लोबल पोजिशनिंग सिस्टम (जीपीएस)। पहला कृत्रिम उपग्रह १९५७ में सोवियत संघ द्वारा लॉन्च किया गया था और इसे स्पटनिक १ कहा गया था।
Related Terms:
See this term in other languages
Term and definition status: The original definition of this term in English have been approved by a research astronomer and a teacher The translation of this term and its definition is still awaiting approval
The OAE Multilingual Glossary is a project of the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education (OAE) in collaboration with the IAU Office of Astronomy Outreach (OAO). The terms and definitions were chosen, written and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits here. All glossary terms and their definitions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE".
If you notice a factual or translation error in this glossary term or definition then please get in touch.
Related Media
Satellite swarm versus night sky beauty, by Torsten Hansen, Germany
Credit: Torsten Hansen/IAU OAE
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Related Activities
Valleys Deep and Mountains High
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Learn how radar altimetry from satellites works and how to put landscapes on paper.
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Maps
, Earth observation
, Sentinel
, Copernicus
, Remote sensing
, Altimetry
, Radar
Age Ranges:
14-16
, 16-19
Education Level:
Middle School
, Secondary
Areas of Learning:
Discussion Groups
, Modelling
, Social Research
Costs:
Medium Cost
Duration:
2 hours
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Analysing and interpreting data
, Asking questions
, Communicating information
, Developing and using models
, Using mathematics and computational thinking
A View from Above
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: How do satellites take images of the Earth surface and how do we analyse and use them?
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Maps
, Climate
, Landsat
, Earth observation
, Sentinel
, Copernicus
, Remote sensing
, Vegetation
Age Ranges:
14-16
, 16-19
Education Level:
Middle School
, Secondary
Areas of Learning:
Social Research
Costs:
Low Cost
Duration:
1 hour 30 mins
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Analysing and interpreting data
, Asking questions
, Communicating information
, Constructing explanations
, Developing and using models
, Engaging in argument from evidence
, Using mathematics and computational thinking
Build Your Own Artificial Satellite
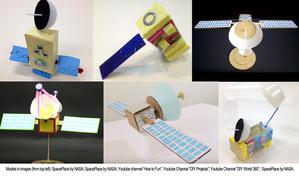
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Build a satellite to learn what they are made of and their uses.
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Art
, Creativity
, Hands-on
, Model
Age Ranges:
8-10
Education Level:
Primary
Areas of Learning:
Discussion Groups
, Interactive Lecture
, Modelling
Costs:
Low Cost
Duration:
1 hour 30 mins
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Communicating information
, Developing and using models
Where on Earth am I?
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: How do satellite-based positioning and GPS navigation work?
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Clocks
, Geography
, Maps
, GPS
, Countries
, Speed of light
, Galileo
Age Ranges:
14-16
Education Level:
Middle School
Areas of Learning:
Guided-discovery learning
, Problem-solving
Costs:
Low Cost
Duration:
1 hour 30 mins
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Analysing and interpreting data
, Asking questions
, Communicating information
, Constructing explanations
, Developing and using models
, Using mathematics and computational thinking