This page describes an image Virgo Constellation Map
Download PDF File (PDF file 188.33 kB)
Diagram caption:
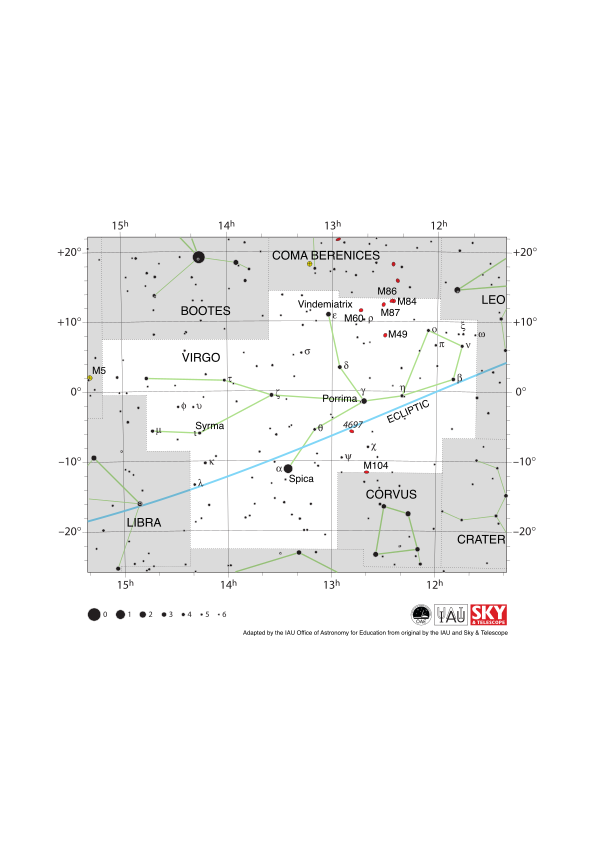
The zodiac constellation Virgo and its surrounding constellations. Starting from the top of the diagram and going clockwise, these are Coma Berenices, Leo, Crater, Corvus, Libra, and Bootes. The brightest star in Virgo, Spica, lies just below the ecliptic (shown here as a blue line) in the middle of the map. One way of locating this star in the night sky is to follow the handle of the Big Dipper to the star Arcturus in Bootes and go along a line straight down to Spica (“arc to Arcturus and spike to Spica”). This star lies just below the ecliptic. The ecliptic is the path the Sun appears to take across the sky over the course of a year. The Sun is in Virgo from mid September to late October. The other planets of the Solar System can often be found in Virgo.
Virgo spans the celestial equator and is thus part of it is visible at some time in the year from all of planet Earth with some of the constellation obscured for the most arctic and antarctic regions of the world. Virgo is most visible in the evenings in the northern hemisphere spring and southern hemisphere autumn.
The constellation Virgo appears as a person lying with their back roughly against the ecliptic, arms outstretched, and feet pointed east. Several deep-sky objects are visible in Virgo, including NGC4697, M49, M87, M86, M84, and M60, all of which are labelled as red ellipses on the map. These are all spiral and elliptical galaxies located several millions of lightyears from Earth. Most notably, M87 is host to the supermassive black hole (Pōwehi) that was imaged by the Event Horizon Telescope in 2019. All of these galaxies are members of the Virgo Cluster, the nearest cluster of galaxies to the Milky Way.
The y-axis of this diagram is in degrees of declination and with north as up and the x-axis is in hours of right ascension with east to the left. The sizes of the stars marked here relate to the star's apparent magnitude, a measure of its apparent brightness. The larger dots represent brighter stars. The Greek letters mark the brightest stars in the constellation. These are ranked by brightness with the brightest star being labelled alpha, the second brightest beta, etc., although this ordering is not always followed exactly. The dotted boundary lines mark the IAU's boundaries of the constellations and the solid green lines mark one of the common forms used to represent the figures of the constellations. Neither the constellation boundaries nor the lines joining the stars appear on the sky.
Diagram credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by IAU/Sky & Telescope. Credit Link
Diagram translation status: Not yet approved by a reviewer
Related glossary terms:
Big Dipper
, Cluster of Galaxies
, Ecliptic
, Elliptical Galaxy
, Leo
, Libra
, Spiral Galaxy
, Supermassive Black Hole
, Virgo
, नक्षत्र
Diagram license: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
The diagram captions presented on the OAE website were written, translated and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits for our translation project here. All media file captions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE". The media files themselves may have different licenses (see above) and should be credited as listed above under "credit".