Glossary term: कक्षा (ऑर्बिट)
Description: ऑर्बिट म्हणजे प्रणालीमध्ये फिरणाऱ्या वस्तूचा असा मार्ग जो त्या प्रणालीच्या वस्तुमानाच्या केंद्राभोवती असतो, जो प्रणालीमधील वस्तूंमधील परस्पर गुरुत्वाकर्षण शक्तीमुळे होतो. सूर्यमालेसारख्या प्रणालींसाठी, जिथे मध्यवर्ती भाग इतर शरीरांपेक्षा खूप मोठा आहे, वस्तुमानाचे हे केंद्र सर्वात मोठ्या वस्तूच्या आत किंवा जवळ असते (सूर्यमालेच्या बाबतीत, सूर्य). बायनरी स्टार सिस्टीममध्ये ताऱ्यांच्या कक्षेतील वस्तुमानाचे केंद्र बहुतेक वेळा दोन ताऱ्यांमध्ये असते.
कक्षा सामान्यत: लंबवर्तुळाकार असतात आणि प्रणालीच्या वस्तुमानाचे केंद्र लंबवर्तुळाच्या एका केंद्रस्थानी असते. कक्षेचा आकारमान आणि आकार हे अर्धमुख्य अक्ष आणि लंबवर्तुळाच्या विलक्षणतेद्वारे परिभाषित केले जातात. अधिक विक्षिप्त कक्षांमध्ये खुप जास्त लंबवर्तुळाची विलक्षणता असतात. सूर्यमालेतील बहुतेक ग्रहांची परिभ्रमण विलक्षणता शून्याच्या अगदी जवळ असते, उदाहरणार्थ, शुक्र (0.007), पृथ्वी (0.017), बुध (0.206) आणि बटू ग्रह प्लूटो (0.244).
Related Terms:
See this term in other languages
Term and definition status: The original definition of this term in English have been approved by a research astronomer and a teacher The translation of this term and its definition is still awaiting approval
The OAE Multilingual Glossary is a project of the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education (OAE) in collaboration with the IAU Office of Astronomy Outreach (OAO). The terms and definitions were chosen, written and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits here. All glossary terms and their definitions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE".
If you notice a factual or translation error in this glossary term or definition then please get in touch.
Related Media
Jupiter's Rotation, by Vishal Sharma, India
Credit: Vishal Sharma/IAU OAE
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Jupiter Moons Movie2, by Nicolas Hurez, Paul-Antoine Matrangolo, and Carl Pennypacker, United States of America
Credit: Nicolas Hurez, Paul-Antoine Matrangolo and Carl Pennypacker/IAU OAE
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Jupiter, Io and its shadow, by Ralf Burkart, Germany
Credit: Ralf Burkart/IAU OAE
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
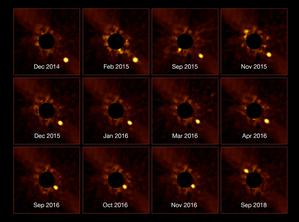
The orbit of beta Pictoris b
Credit: ESO/Lagrange/SPHERE consortium credit link
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Related Activities
Measure the Solar Diameter
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Hands-on activity to measure the Sun by using household materials.
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Hands-on
, Scales
, Observing
, Measurement
Age Ranges:
12-14
, 14-16
, 16-19
, 19+
Education Level:
Middle School
Areas of Learning:
Social Research
Costs:
Low Cost
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Communicating information
, Constructing explanations
, Using mathematics and computational thinking
Blue Marble in Empty Space
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Students are taken on a virtual journey to outer space to experience that we live on a tiny planet that floats in a vast and empty space.
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Life
, Hands-on
, Model
, Scales
, Distances
, ISS
Age Ranges:
6-8
, 8-10
Education Level:
Primary
, Secondary
Areas of Learning:
Interactive Lecture
, Modelling
Costs:
Low Cost
Duration:
30 mins
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Asking questions
, Communicating information
, Developing and using models
Lunar Day
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Through a fun-learning activity, understand why moon always keeps the same face towards Earth.
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Lunar day
Age Ranges:
4-6
, 6-8
Education Level:
Primary
, Secondary
Areas of Learning:
Modelling
, Structured-inquiry learning
Costs:
Free
Duration:
30 mins
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Analysing and interpreting data
, Asking questions
, Communicating information
, Constructing explanations
, Developing and using models
Day and Night in the World
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Compare diurnal and nocturnal animals and experiment with day and night.
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Life
, Model
, Animals
, Day and night
Age Ranges:
6-8
, 8-10
Education Level:
Primary
Areas of Learning:
Interactive Lecture
, Modelling
, Social Research
Costs:
Low Cost
Duration:
1 hour
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Asking questions
, Constructing explanations
, Developing and using models
, Planning and carrying out investigations
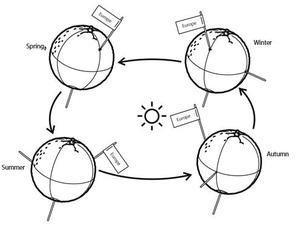
Seasons Around the World
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Demonstrate the seasons on Earth using a model.
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Hands-on
, Model
Age Ranges:
6-8
, 8-10
, 10-12
Education Level:
Middle School
, Primary
Areas of Learning:
Modelling
, Social Research
Costs:
Medium Cost
Duration:
45 mins
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Analysing and interpreting data
, Asking questions
, Constructing explanations
, Developing and using models
, Planning and carrying out investigations