Glossary term: Declinação
Description: Nos sistemas de coordenadas equatoriais, a declinação é uma das duas coordenadas usadas para especificar a posição de um objeto no céu. Especificamente, a declinação é a distância angular do objeto em relação ao equador celeste, geralmente medida em graus: positiva para objetos no hemisfério norte, e negativa para objetos no hemisfério sul. Dessa forma, a declinação é análoga à latitude geográfica na superfície da Terra. O equador celeste corresponde aproximadamente à projeção do equador da Terra na esfera celeste, mas os sistemas de coordenadas modernos, como o Sistema Internacional de Referência Celeste (ICRS), definem o equador celeste sem referência à Terra, usando como referência as posições de objetos celestes muito distantes no céu.
Related Terms:
See this term in other languages
Term and definition status: The original definition of this term in English have been approved by a research astronomer and a teacher The translation of this term and its definition is still awaiting approval
The OAE Multilingual Glossary is a project of the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education (OAE) in collaboration with the IAU Office of Astronomy Outreach (OAO). The terms and definitions were chosen, written and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits here. All glossary terms and their definitions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE".
If you notice a factual or translation error in this glossary term or definition then please get in touch.
Related Diagrams
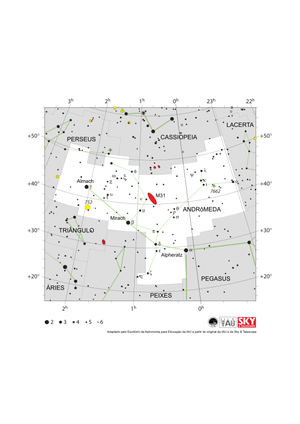
Mapa da Constelação de Andrômeda
Credit: Adaptado pelo Escritório de Astronomia para Educação da IAU a partir do original da IAU/Sky & Telescope
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
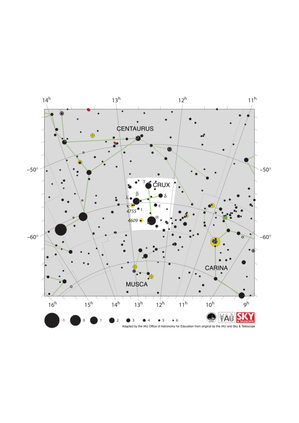
Crux Constellation Map
Credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by IAU/Sky & Telescope.
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
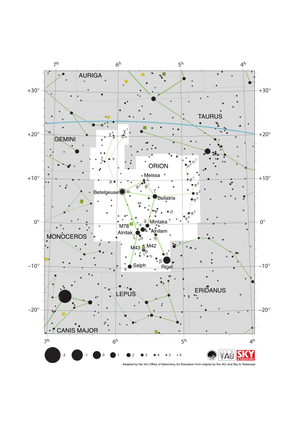
Orion Constellation Map
Credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by IAU/Sky & Telescope
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Libra Constellation Map
Credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by IAU/Sky & Telescope
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
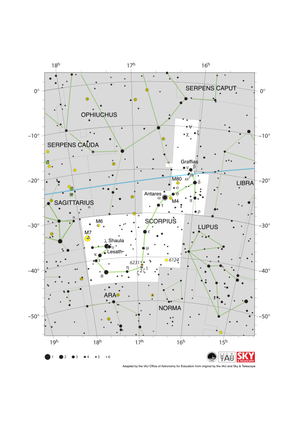
Scorpius Constellation Map
Credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by IAU/Sky & Telescope
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons