Glossary term: 双子座
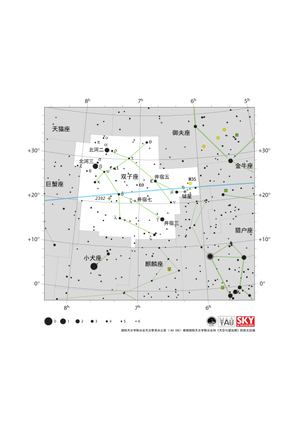
Description: 双子座是黄道带上的13个星座之一,也是国际天文学联合会定义的88个现代星座之一,但其历史可以追溯到更久远的年代——它是公元2世纪的天文学家克罗狄斯·托勒密(Claudius Ptolemy)命名的48个星座之一。双子座的名字来源于它最亮的两颗星——北河二和北河三,在巴比伦神话中,他们是一对双胞胎神祇。双子座在北半球冬季可见,位于金牛座和巨蟹座之间。世界各地的许多文化中,都存在着与双子座及其恒星有关的传说。北河二和北河三分别距离地球约50光年和30光年。肉眼可以看到双子座的约80颗恒星。位于双子座天区内的著名深空天体有M35、NGC 2158、NGC 2392和Abell 21等。
Related Terms:
See this term in other languages
Term and definition status: The original definition of this term in English have been approved by a research astronomer and a teacher The translation of this term and its definition is still awaiting approval
The OAE Multilingual Glossary is a project of the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education (OAE) in collaboration with the IAU Office of Astronomy Outreach (OAO). The terms and definitions were chosen, written and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits here. All glossary terms and their definitions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE".
If you notice a factual or translation error in this glossary term or definition then please get in touch.
Related Media
夜空中最亮的星
Credit: Giorgia Hofer/IAU OAE
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
猎户座,摄于罗马尼亚
Credit: Alex Conu/IAU OAE
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
双子座火球
Credit: 戴建峰/国际天文学联合会教育办公室 (CC BY 4.0)
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Related Diagrams
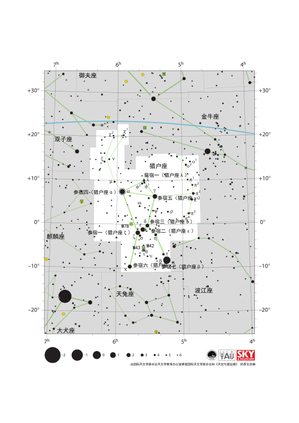
猎户座星图
Credit: 由国际天文学联合会天文教育办公室根据国际天文学联合会/《天空与望远镜》的原文改编
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
金牛座星图
Credit: 国际天文学联合会天文教育办公室(IAU OAE)根据国际天文学联合会和《天空与望远镜》的原文改编
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
巨蟹座星图
Credit: 国际天文学联合会天文教育办公室(IAU OAE)根据国际天文学联合会和《天空与望远镜》的原文改编
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
双子座星图
Credit: 国际天文学联合会天文教育办公室(IAU OAE)根据国际天文学联合会和《天空与望远镜》的原文改编
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
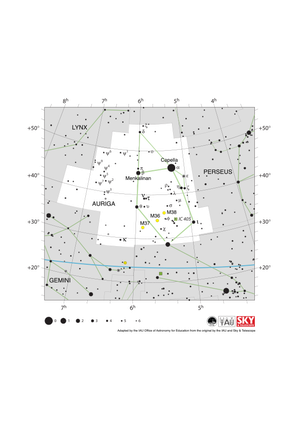
Auriga Constellation Map
Credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by the IAU and Sky & Telescope
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons