Glossary term: 全球气候变暖
Description: 全球气候变暖是指水分子、二氧化碳、甲烷等温室气体使地球大气变暖。其原因是温室效应增强,大气层捕获了更多的红外辐射,从而提高了全球平均温度。温室气体的来源可以是天然的,也可以是(在地球上)人类工业活动造成的。地球上的全球变暖将对地球产生重大的长期影响,包括当地气候模式的短期和中期变化、栖息地破坏和海平面上升。
Related Terms:
See this term in other languages
Term and definition status: The original definition of this term in English have been approved by a research astronomer and a teacher The translation of this term and its definition is still awaiting approval
The OAE Multilingual Glossary is a project of the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education (OAE) in collaboration with the IAU Office of Astronomy Outreach (OAO). The terms and definitions were chosen, written and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits here. All glossary terms and their definitions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE".
If you notice a factual or translation error in this glossary term or definition then please get in touch.
Related Activities
Continental Climate and Oceanic Climate
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Find out why, in the summer it is cooler by the sea than on the land!
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Climate change
, Climate
, Ocean
Age Ranges:
6-8
, 8-10
Education Level:
Primary
Areas of Learning:
Modelling
, Social Research
, Traditional Science Experiment
Costs:
Medium Cost
Duration:
45 mins
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Analysing and interpreting data
, Asking questions
, Constructing explanations
, Engaging in argument from evidence
, Planning and carrying out investigations
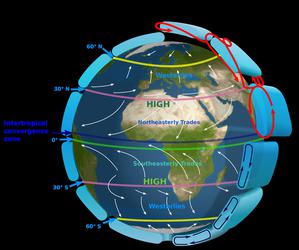
The Intertropical Convergence Zone
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: The air circulation system: how are winds created?
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Climate
, Updraft
, Convection
, Winds
Age Ranges:
12-14
, 14-16
Education Level:
Middle School
Areas of Learning:
Discussion Groups
, Modelling
, Social Research
Costs:
Medium Cost
Duration:
1 hour
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Communicating information
, Constructing explanations
, Developing and using models
, Engaging in argument from evidence
, Planning and carrying out investigations
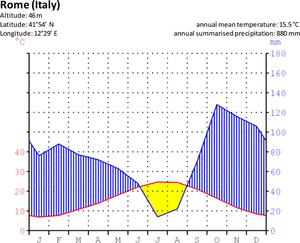
The Climate in Numbers and Graphs
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Learn about climate from data and graphs
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Climate
, Average
, Climate zone
, Weather
Age Ranges:
14-16
, 16-19
Education Level:
Secondary
Areas of Learning:
Social Research
Costs:
Low Cost
Duration:
2 hours
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Analysing and interpreting data
, Asking questions
, Communicating information
, Constructing explanations
, Developing and using models
, Engaging in argument from evidence
, Using mathematics and computational thinking
Oceans As A Heat Reservoir
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Why do oceans play an important role in mitigating global warming?
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Life
, Climate change
, Oceans
, heat
Age Ranges:
12-14
, 14-16
, 16-19
Education Level:
Middle School
Areas of Learning:
Modelling
, Social Research
, Traditional Science Experiment
Costs:
Medium Cost
Duration:
1 hour 30 mins
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Analysing and interpreting data
, Constructing explanations
, Developing and using models
, Engaging in argument from evidence
, Planning and carrying out investigations
The Big Meltdown
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Learn what would happen on Earth if all the ice melted!
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Life
, Climate change
, Remote sensing
, Oceans
, Water
, Antarctic
, Arctic
, Ice
, Archimedes
Age Ranges:
8-10
, 10-12
, 12-14
Education Level:
Middle School
, Primary
, Secondary
Areas of Learning:
Discussion Groups
, Modelling
, Social Research
, Traditional Science Experiment
Costs:
Medium Cost
Duration:
45 mins
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Analysing and interpreting data
, Asking questions
, Communicating information
, Constructing explanations
, Developing and using models
, Engaging in argument from evidence
, Planning and carrying out investigations