Glossary term: 视星等
Description: 视星等是观测者看到的天体亮度的量度。由于历史原因,星等表将较大的数字分配给较暗的天体。星等是一个对数刻度,5 个星等的差异相当于测量亮度的 100 倍。由于亮度可以用不同的波长和不同的技术测量,因此有许多震级标度。常用的 "视星等 "刻度是这样设定的:明亮的织女星的视星等为零。在这个星等表上,夜空中最亮的恒星天狼星的星等为-1.46,太阳和满月的星等分别为-26.7 和-12.7。负数表示这些天体看起来比织女星更亮。在非常暗的条件下,视力极好的人可以看到约 6 等的恒星。哈勃超深视场的视星等接近 31 等。这比 6 等暗大约 100 到 5 的幂,或者说比 6 等暗 10,000,000,000 倍。
视星等是用来衡量天体在观测者眼中亮度的一种度量。由于历史原因,星等标尺将较大的数字分配给较暗的天体。视星等是一个对数刻度,星等相差5个单位时,亮度相差100倍。因为亮度可以在不同波长和通过不同技术进行测量,所以有多种星等标尺。常见的“视星等”尺度设定明亮的织女星视星等为0。在该标尺上,夜空中最亮的恒星天狼星的视星等为-1.46,太阳和满月的视星等分别为-26.7和-12.7。负数表示这些天体比织女星更亮。在非常黑暗的条件下,视力极佳的人可以看到视星等约为6的恒星。而哈勃超深空的视星等接近31,这比视星等为6的恒星暗约100的五次方,即100亿倍。
Related Terms:
See this term in other languages
Term and definition status: The original definition of this term in English have been approved by a research astronomer and a teacher The translation of this term and its definition is still awaiting approval
The OAE Multilingual Glossary is a project of the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education (OAE) in collaboration with the IAU Office of Astronomy Outreach (OAO). The terms and definitions were chosen, written and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits here. All glossary terms and their definitions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE".
If you notice a factual or translation error in this glossary term or definition then please get in touch.
Related Diagrams
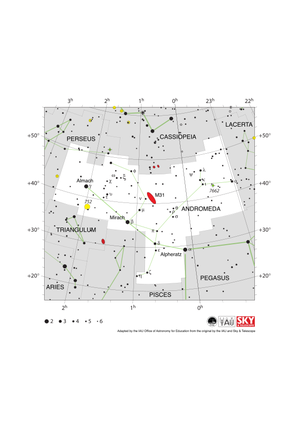
Andromeda Constellation Map
Credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by IAU/Sky & Telescope
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
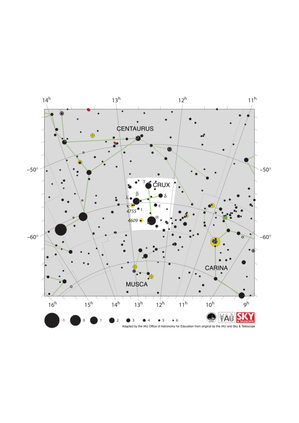
Crux Constellation Map
Credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by IAU/Sky & Telescope.
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
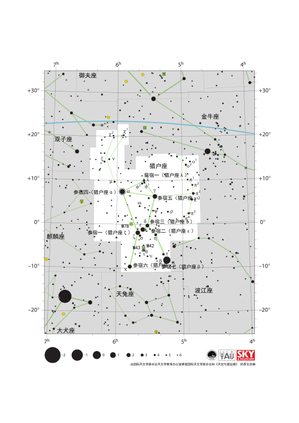
猎户座星图
Credit: 由国际天文学联合会天文教育办公室根据国际天文学联合会/《天空与望远镜》的原文改编
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
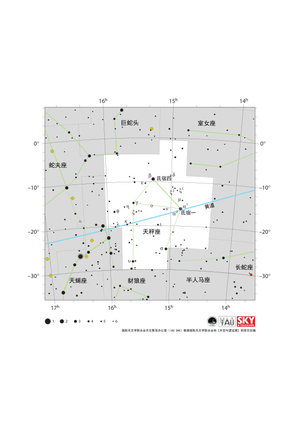
天秤座星图
Credit: 国际天文学联合会天文教育办公室(IAU OAE)根据国际天文学联合会和《天空与望远镜》的原文改编
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
天蝎座星图
Credit: 国际天文学联合会天文教育办公室(IAU OAE)根据国际天文学联合会和《天空与望远镜》的原文改编
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons