Glossary term: 月球
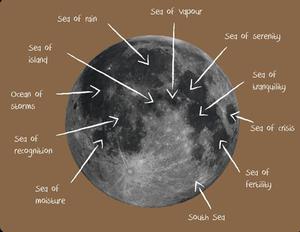
Description: 月球是自身并不发光的天体,但它会反射落在其上的太阳光。这就产生了月球特有的月相。月球是地球唯一的主要天然卫星,其大小和质量在太阳系内的所有天然卫星中排名第五。在英文中,首字母大写的“Moon”表示月球,而首字母小写的“moon”则表示太阳系内外的其他天然卫星。与太阳系内的其他卫星相比,月球的体积相对于它所环绕行星的体积的占比是最大的。月球沿围绕地球的椭圆轨道运行,与地球的平均距离为38.4万千米。月球没有大气层,物质组分与地球类似,内核富含铁,外层为岩石。这种相似并非偶然:据我们所知,大约45亿年前,地球和一颗火星大小的行星碰撞,产生的碎片最终形成了月球,它的大部分物质来自最初的地球地幔。月球表面既有被称为“月海”的深色区域,也有浅色高地,并布满了陨击坑。月球表面积为3.79×107平方千米,体积为2.20×1010立方千米,质量为7.35×1022千克。月球围绕地球运行的轨道周期的确切数值取决于参考系:相对于遥远的恒星,月球每27.3天运行一圈(“恒星月”)。对于地球上的观测者来说,两个新月之间的间隔时间为29.5天(“朔望月”)。
Related Terms:
See this term in other languages
Term and definition status: The original definition of this term in English have been approved by a research astronomer and a teacher The translation of this term and its definition is still awaiting approval
The OAE Multilingual Glossary is a project of the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education (OAE) in collaboration with the IAU Office of Astronomy Outreach (OAO). The terms and definitions were chosen, written and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits here. All glossary terms and their definitions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE".
If you notice a factual or translation error in this glossary term or definition then please get in touch.
Related Media
阿波罗 11 号任务的月面活动
Credit: 美国国家航空航天局/阿波罗项目档案 credit link
License: PD Public Domain icons
塞勒涅与月亮相遇,作者Sheila Wiwchar,加拿大
Credit: Sheila Wiwchar/IAU OAE
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
红月,法国丹尼尔·亨利昂作品
Credit: 丹尼尔·亨利/国际天文学联合会教育办公室
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
正发生月食的月亮从多洛米蒂山脉(联合国教科文组织世界遗产区)普伦德拉岩峰(Rochetta di Prendera )附近落下,作者 Alessandra Masi,意大利
Credit: Alessandra Masi/IAU OAE
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Related Activities
Lunar Landscape
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Create craters and explore the lunar landscape with this hands-on activity.
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Hands-on
, Model
, Lunar landscape
, Craters
Age Ranges:
4-6
, 6-8
, 8-10
Education Level:
Primary
Areas of Learning:
Modelling
Costs:
Medium Cost
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Asking questions
, Communicating information
, Developing and using models
Meet Our Neighbours: Moon
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Explore the tactile version of our moon with household materials.
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Hands-on
, Model
, Visually Impaired
, Tactile
Age Ranges:
6-8
, 8-10
, 10-12
Education Level:
Middle School
, Primary
, Secondary
Areas of Learning:
Interactive Lecture
, Modelling
Costs:
Low Cost
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Analysing and interpreting data
, Asking questions
, Communicating information
, Developing and using models
Lunar Day
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Through a fun-learning activity, understand why moon always keeps the same face towards Earth.
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Lunar day
Age Ranges:
4-6
, 6-8
Education Level:
Primary
, Secondary
Areas of Learning:
Modelling
, Structured-inquiry learning
Costs:
Free
Duration:
30 mins
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Analysing and interpreting data
, Asking questions
, Communicating information
, Constructing explanations
, Developing and using models
Sun, Earth and Moon Model
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Build an Earth-Moon-Sun mobile to learn about how they orbit.
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Hands-on
, Model
Age Ranges:
8-10
Education Level:
Primary
Areas of Learning:
Game-mediated learning
, Modelling
, Social Research
Costs:
Medium Cost
Duration:
1 hour 30 mins
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Asking questions
, Communicating information
, Developing and using models
Children's Planetary Maps: The Moon
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: An up close look at our own satellite
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Maps
, Planetary cartography
, Spatial thinking
Age Ranges:
6-8
, 8-10
, 10-12
, 12-14
Education Level:
Middle School
, Primary
, Secondary
Areas of Learning:
Social Research
Costs:
Low Cost
Duration:
2 hours
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Analysing and interpreting data
, Asking questions
, Communicating information
, Constructing explanations
, Developing and using models
, Engaging in argument from evidence
, Planning and carrying out investigations