Glossary term: 人造卫星
Description: 人造卫星是一种人造装置,它被送入太空,绕地球或其他太阳系天体运行,并在引力作用下保持在轨道上。人造卫星可以执行各种任务,包括航拍地球照片,帮助气象学家预测天气,或拍摄天体和遥远星系的照片,帮助科学家更好地了解宇宙系统。人造卫星还主要用于全球通信和定位,如全球定位系统(GPS)。第一颗人造卫星于 1957 年由苏联发射升空,被称为“斯普特尼克”1号。
Related Terms:
See this term in other languages
Term and definition status: The original definition of this term in English have been approved by a research astronomer and a teacher The translation of this term and its definition is still awaiting approval
The OAE Multilingual Glossary is a project of the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education (OAE) in collaboration with the IAU Office of Astronomy Outreach (OAO). The terms and definitions were chosen, written and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits here. All glossary terms and their definitions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE".
If you notice a factual or translation error in this glossary term or definition then please get in touch.
Related Media
卫星群与夜空之美,作者 Torsten Hansen,德国
Credit: Torsten Hansen/IAU OAE
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Related Activities
Valleys Deep and Mountains High
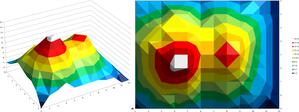
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Learn how radar altimetry from satellites works and how to put landscapes on paper.
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Maps
, Earth observation
, Sentinel
, Copernicus
, Remote sensing
, Altimetry
, Radar
Age Ranges:
14-16
, 16-19
Education Level:
Middle School
, Secondary
Areas of Learning:
Discussion Groups
, Modelling
, Social Research
Costs:
Medium Cost
Duration:
2 hours
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Analysing and interpreting data
, Asking questions
, Communicating information
, Developing and using models
, Using mathematics and computational thinking
A View from Above
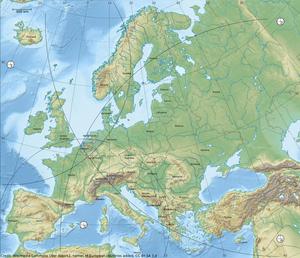
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: How do satellites take images of the Earth surface and how do we analyse and use them?
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Maps
, Climate
, Landsat
, Earth observation
, Sentinel
, Copernicus
, Remote sensing
, Vegetation
Age Ranges:
14-16
, 16-19
Education Level:
Middle School
, Secondary
Areas of Learning:
Social Research
Costs:
Low Cost
Duration:
1 hour 30 mins
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Analysing and interpreting data
, Asking questions
, Communicating information
, Constructing explanations
, Developing and using models
, Engaging in argument from evidence
, Using mathematics and computational thinking
Build Your Own Artificial Satellite
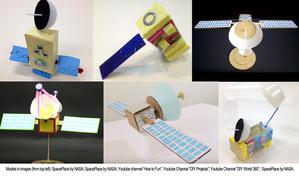
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Build a satellite to learn what they are made of and their uses.
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Art
, Creativity
, Hands-on
, Model
Age Ranges:
8-10
Education Level:
Primary
Areas of Learning:
Discussion Groups
, Interactive Lecture
, Modelling
Costs:
Low Cost
Duration:
1 hour 30 mins
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Communicating information
, Developing and using models
Where on Earth am I?
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: How do satellite-based positioning and GPS navigation work?
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Clocks
, Geography
, Maps
, GPS
, Countries
, Speed of light
, Galileo
Age Ranges:
14-16
Education Level:
Middle School
Areas of Learning:
Guided-discovery learning
, Problem-solving
Costs:
Low Cost
Duration:
1 hour 30 mins
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Analysing and interpreting data
, Asking questions
, Communicating information
, Constructing explanations
, Developing and using models
, Using mathematics and computational thinking