Glossary term: 天蝎座
Description: 天蝎座是黄道带上的13个星座之一。组成这个星座的恒星位于与黄道(由地球绕太阳运行的轨迹所确定的平面)相交的那部分天空。事实上,黄道带上的所有星座都与黄道相交。从地球上看,我们会发现太阳和太阳系的其他行星经常落在天蝎座中。天蝎座是国际天文学联合会承认的88个星座之一,也是托勒密最初确定的48个星座之一。早在托勒密之前一千多年,苏美尔人就已经确定了天蝎座。在其他文化中,天蝎座有着不同的名称:在毛利和波利尼西亚文化中,天蝎座被称为毛伊的钩子;而澳大利亚土著群体,如阿纳姆地区的约尔努人,则将天蝎座视为鳄鱼和蝎子。天蝎座最亮的恒星是大火星(又称心宿二、天蝎座α),它是一颗红巨星,距离地球约550光年。
Related Terms:
See this term in other languages
Term and definition status: The original definition of this term in English have been approved by a research astronomer and a teacher The translation of this term and its definition is still awaiting approval
The OAE Multilingual Glossary is a project of the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education (OAE) in collaboration with the IAU Office of Astronomy Outreach (OAO). The terms and definitions were chosen, written and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits here. All glossary terms and their definitions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE".
If you notice a factual or translation error in this glossary term or definition then please get in touch.
Related Media
猴面包树大道上空的银河
Credit: Amirreza Kamkar/IAU OAU
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
驾驶途中
Credit: Marcin Zajac/IAU OAE
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
安波塞利国家公园上空的银河拱门
Credit: Amirreza Kamkar/IAU OAE
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
横贯天顶的银河
Credit: Ohnishi Kouji/IAU OAE
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
尼加拉瓜马萨亚省宁迪里镇的星空
Credit: René Antonio Urroz Álvarez/IAU OAE
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Related Diagrams
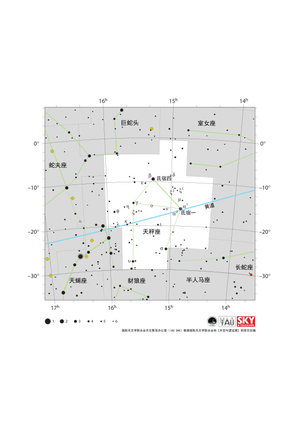
天秤座星图
Credit: 国际天文学联合会天文教育办公室(IAU OAE)根据国际天文学联合会和《天空与望远镜》的原文改编
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
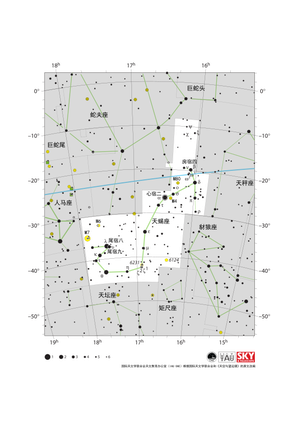
天蝎座星图
Credit: 国际天文学联合会天文教育办公室(IAU OAE)根据国际天文学联合会和《天空与望远镜》的原文改编
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
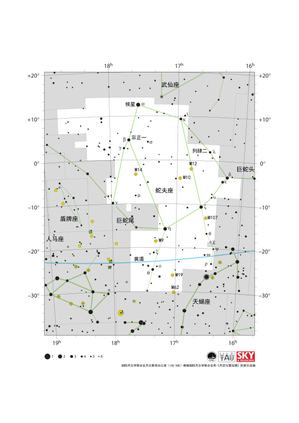
人马座星图
Credit: 国际天文学联合会天文教育办公室(IAU OAE)根据国际天文学联合会和《天空与望远镜》的原文改编
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
蛇夫座星图
Credit: 国际天文学联合会天文教育办公室(IAU OAE)根据国际天文学联合会和《天空与望远镜》的原文改编
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
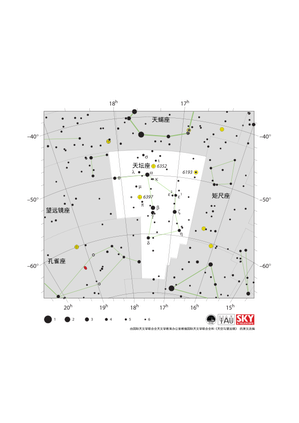
天坛座星图
Credit: 由国际天文学联合会天文教育办公室根据国际天文学联合会/《天空与望远镜》的原文改编
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons