Glossary term: 时间
Description: 我们每个人对时间都有一个基本的概念:从过去到现在,再到未来,事件一个接一个地发生。然而,时间并不是看得见、听得到、闻得到、摸得到或尝得到的东西。不过,它是可以测量的,而这正是时间在天文学和物理学中的重要性所在。
我们测量时间的方法是,将正在发生的事情的持续时间与时钟上测量的持续时间进行比较,或者,对于较长的时间,与日历上测量的持续时间进行比较。传统上,这种时间测量是以地球自转为基础的。地球自转一圈所需的时间(根据太阳的位置判断)就是一天的长度。通常的会讲一天分为 24 小时,每小时分为 60 分钟,每分钟分为 60 秒,这提供了额外的时间单位。
自 1967 年起,时间的定义改用铯-133 原子钟测量的一秒时间("SI 秒")。在此基础上定义了几种时间系统,特别是世界时间(UTC),它被用于全世界的官方计时;还有所谓的儒略日及其变体,它是天文学中使用的一种连续计数天数的方法。
爱因斯坦的狭义相对论和广义相对论表明,时钟上流逝的时间既取决于时钟的运动,也取决于重力的影响。这些相对论效应需要在高精度的时间测量中加以考虑,例如使用全球定位系统(GPS)卫星进行的测量。
Related Terms:
See this term in other languages
Term and definition status: The original definition of this term in English have been approved by a research astronomer and a teacher The translation of this term and its definition is still awaiting approval
The OAE Multilingual Glossary is a project of the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education (OAE) in collaboration with the IAU Office of Astronomy Outreach (OAO). The terms and definitions were chosen, written and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits here. All glossary terms and their definitions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE".
If you notice a factual or translation error in this glossary term or definition then please get in touch.
Related Activities
Sun’s Shadow
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Why is the Sun's shadow so important?
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Hands-on
, Shadows
Age Ranges:
6-8
, 8-10
, 10-12
, 12-14
, 14-16
Education Level:
Informal
, Middle School
, Primary
, Secondary
Areas of Learning:
Observation based
, Social Research
Costs:
Medium Cost
Duration:
1 day
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Asking questions
, Communicating information
, Constructing explanations
, Engaging in argument from evidence
Day and Night in the World
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Compare diurnal and nocturnal animals and experiment with day and night.
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Life
, Model
, Animals
, Day and night
Age Ranges:
6-8
, 8-10
Education Level:
Primary
Areas of Learning:
Interactive Lecture
, Modelling
, Social Research
Costs:
Low Cost
Duration:
1 hour
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Asking questions
, Constructing explanations
, Developing and using models
, Planning and carrying out investigations
What Is Time?
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Build an hourglass to understand what time is and how it can be measured.
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Hands-on
, Measurement
, Day and night
, Measure
, Instruments
Age Ranges:
6-8
, 8-10
, 10-12
Education Level:
Middle School
, Primary
Areas of Learning:
Modelling
, Problem-solving
, Social Research
Costs:
Medium Cost
Duration:
1 hour
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Asking questions
, Developing and using models
, Planning and carrying out investigations
Making a Sundial
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Build a sundial and discover how time can be measured.
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Hands-on
, Measurement
, Measure
, History
, Clocks
Age Ranges:
6-8
, 8-10
, 10-12
Education Level:
Middle School
, Primary
Areas of Learning:
Modelling
, Observation based
, Social Research
Costs:
Medium Cost
Duration:
1 hour
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Analysing and interpreting data
, Asking questions
, Communicating information
, Developing and using models
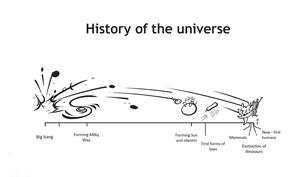
History of the Universe
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Build a timeline of the all Universe!
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
History
, Timeline
, Mathematics
, Humans
Age Ranges:
8-10
, 10-12
, 12-14
Education Level:
Middle School
, Primary
Areas of Learning:
Problem-solving
, Social Research
Costs:
Low Cost
Duration:
1 hour 30 mins
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Asking questions
, Communicating information
, Developing and using models
, Using mathematics and computational thinking