Glossary term: 北斗七星
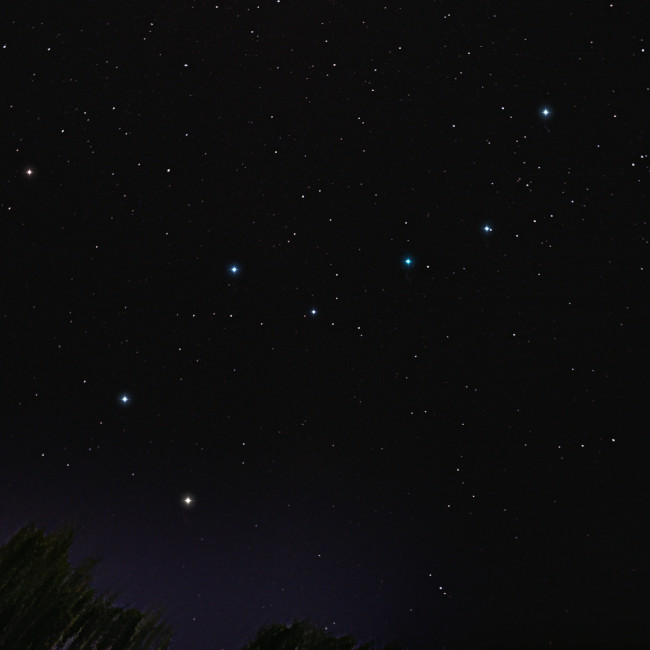
Description: 北斗七星是一个著名的星宿(更准确的术语是星群),它是位于北天大熊座的一部分。北斗七星实际上是由八颗星组成:天枢(Dubhe)、天璇(Merak)、天玑(Phecda)、天权(Megrez)、玉衡(Alioth)、开阳(Mizar/Alcor)和摇光(Alkaid)。其中,开阳和辅星(Alcor)是一对双星。北斗七星的斗口两颗星(天枢和天璇)可以用来指引北极星(Polaris)的位置。由于这八颗星的亮度相近,北斗七星在夜空中特别显眼(尽管天权和辅星的亮度稍微比其他星弱一些),因此在许多文化中都有不同的名称。北斗七星的中间五颗星属于一个正在太空中共同运动的恒星群,即大熊座星宿。其中,天枢呈现红色,其他七颗星则为白色。
Related Terms:
See this term in other languages
Term and definition status: The original definition of this term in English have been approved by a research astronomer and a teacher The translation of this term and its definition is still awaiting approval
The OAE Multilingual Glossary is a project of the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education (OAE) in collaboration with the IAU Office of Astronomy Outreach (OAO). The terms and definitions were chosen, written and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits here. All glossary terms and their definitions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE".
If you notice a factual or translation error in this glossary term or definition then please get in touch.
Related Media
世界各处的星座
Credit: Stephanie Ye Ziyi/IAU OAE
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
北斗七星
Credit: Arya Anthony/IAU OAE
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
如梦如幻的星空和气流
Credit: Likai Lin/IAU OAU
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
四季的北斗
Credit: Giorgia Hofer/IAU OAE
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
北斗七星和新智彗星 C2020 F3
Credit: 乔尔贾·霍弗/国际天文学联合会教育办公室 (CC BY 4.0)
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Related Diagrams
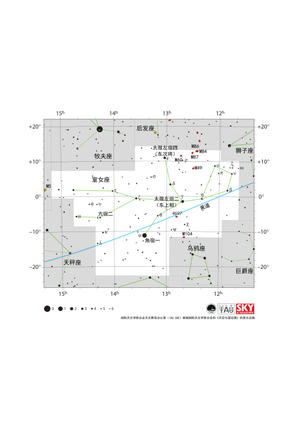
室女座星图
Credit: 国际天文学联合会天文教育办公室(IAU OAE)根据国际天文学联合会和《天空与望远镜》的原文改编
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
大熊座星图
Credit: 国际天文学联合会天文教育办公室(IAU OAE)根据国际天文学联合会和《天空与望远镜》的原文改编
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Related Activities
Moving constellations
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Let's learn how stars in constellations move through time using real astronomical images.
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Software
, Data analysis
, stellarium
, gaia
, hipparcos
, ursa major
Age Ranges:
10-12
, 12-14
, 14-16
, 16-19
, 19+
Education Level:
Middle School
, Secondary
Areas of Learning:
Guided-discovery learning
, Observation based
, Technology-based
Costs:
Free
Duration:
3 hours
Skills:
Analysing and interpreting data
, Asking questions
, Communicating information
, Developing and using models
, Engaging in argument from evidence