Glossary term: 红移
Description: 这个术语可以指三种不同的效应:多普勒红移、宇宙学红移或引力红移。多普勒红移与蓝移相反;在红移的情况下,发射电磁辐射的源远离观察者,因此电磁辐射被拉伸到更长(更红)的波长。这类似于声波中的多普勒效应。宇宙学红移是源发射的电磁辐射因空间的物理膨胀而被拉伸到更长波长的结果,与相对运动引起的多普勒红移不同。引力红移指的是源发出的电磁辐射被拉伸到更长波长的效应,或者说光子在试图离开引力更强的区域(引力井)时失去能量。
Related Terms:
See this term in other languages
Term and definition status: The original definition of this term in English have been approved by a research astronomer and a teacher The translation of this term and its definition is still awaiting approval
The OAE Multilingual Glossary is a project of the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education (OAE) in collaboration with the IAU Office of Astronomy Outreach (OAO). The terms and definitions were chosen, written and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits here. All glossary terms and their definitions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE".
If you notice a factual or translation error in this glossary term or definition then please get in touch.
Related Media
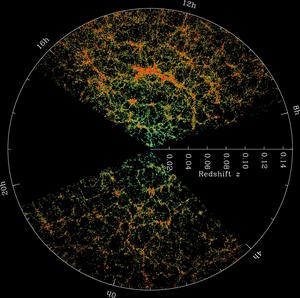
SDSS 红移分布图
Credit: M.布兰顿和斯隆数字巡天 credit link
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons