Glossary term: 拱极星
Description: 在地球上的大多数地方,都能在地平线以上一定距离的天空中看到北天极或南天极。对于处于这样一个位置的观测者来说,随着时间的流逝,星星似乎在围绕着天极旋转:每颗恒星都在天空中划出一个圆圈,其中心是地轴指向的天极。在圆圈与观测者地平线相交的两点,即东点和西点,该恒星将分别升起和落下。对于距离天极足够近的恒星,其划出的圆圈将完全位于地平线之上。我们的观测者将永远看不到这些恒星升起或落下。这些永不落下的恒星被称为拱极星。
哪些恒星是拱极星取决于观测者的地理纬度和恒星的赤纬——后者是恒星所在位置与天赤道之间的夹角。在北半球,如果一颗恒星的赤纬大于90°减去观测者的地理纬度,那么它就是拱极星。在南半球,我们需要考虑到地理南纬和恒星的南赤纬都带有负号。考虑到这些负号,在南半球,如果一颗恒星的赤纬小于-90°减去观测者的地理纬度,那么它就是拱极星。
Related Terms:
See this term in other languages
Term and definition status: The original definition of this term in English have been approved by a research astronomer and a teacher The translation of this term and its definition is still awaiting approval
The OAE Multilingual Glossary is a project of the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education (OAE) in collaboration with the IAU Office of Astronomy Outreach (OAO). The terms and definitions were chosen, written and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits here. All glossary terms and their definitions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE".
If you notice a factual or translation error in this glossary term or definition then please get in touch.
Related Media
石阵与星环,巨石阵上方的星轨,作者:Till Credner,德国
Credit: Till Credner/IAU OAE
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
半日北极星曝光图,作者:来自意大利的法布里齐奥-梅兰德里
Credit: 法布里齐奥-梅兰德里/国际天文学联合会教育办公室
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
如梦如幻的星空和气流
Credit: Likai Lin/IAU OAU
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
四季的北斗
Credit: Giorgia Hofer/IAU OAE
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
北斗七星和新智彗星 C2020 F3
Credit: 乔尔贾·霍弗/国际天文学联合会教育办公室 (CC BY 4.0)
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Related Diagrams
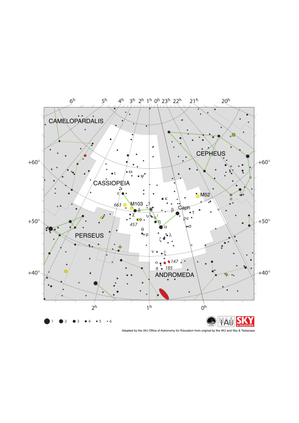
Cassiopeia Constellation Map
Credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by IAU/Sky & Telescope
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
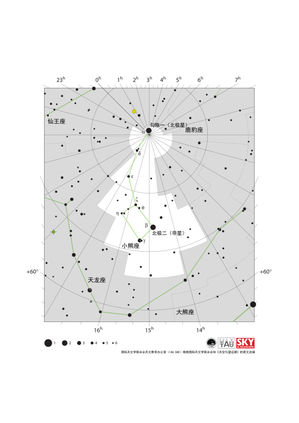
小熊座星图
Credit: 国际天文学联合会天文教育办公室(IAU OAE)根据国际天文学联合会和《天空与望远镜》的原文改编
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
大熊座星图
Credit: 国际天文学联合会天文教育办公室(IAU OAE)根据国际天文学联合会和《天空与望远镜》的原文改编
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
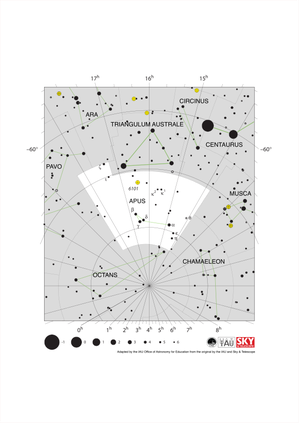
Apus Constellation Map
Credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by IAU/Sky & Telescope
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
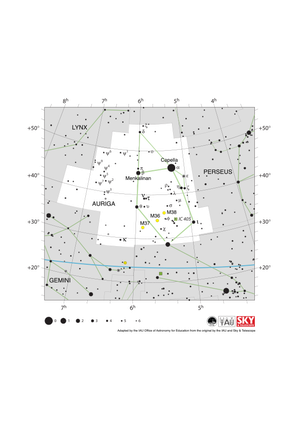
Auriga Constellation Map
Credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by the IAU and Sky & Telescope
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Related Activities
Navigation in the Ancient Mediterranean and Beyond
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Learn the ancient skill of Celestial Navigation
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
History
, Geography
, Celestial navigation
Age Ranges:
14-16
, 16-19
Education Level:
Middle School
, Secondary
Areas of Learning:
Discussion Groups
, Modelling
, Social Research
Costs:
Low Cost
Duration:
1 hour 30 mins
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Analysing and interpreting data
, Asking questions
, Communicating information
, Developing and using models
, Planning and carrying out investigations
, Using mathematics and computational thinking