Glossary term: 宇宙学
Description: 宇宙学源自希腊语 kosmos(和谐或秩序)和 logos(思想或理性)。宇宙学起源于哲学与宗教;世界各地的各种文化都有自己的宇宙学,旨在解释和理解宇宙。多年来,宇宙学已发展成为一门精密的观测科学。先进的地基和空间观测站的建设,加上开创性的理论研究和计算机模拟,使精确宇宙学成为可能。宇宙学作为一门科学,旨在通过了解宇宙内部运行的基本物理机制,在宇宙这一最大尺度上了解整个宇宙的演化历史、形成、结构和未来演化。
Related Terms:
See this term in other languages
Term and definition status: The original definition of this term in English have been approved by a research astronomer and a teacher The translation of this term and its definition is still awaiting approval
The OAE Multilingual Glossary is a project of the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education (OAE) in collaboration with the IAU Office of Astronomy Outreach (OAO). The terms and definitions were chosen, written and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits here. All glossary terms and their definitions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE".
If you notice a factual or translation error in this glossary term or definition then please get in touch.
Related Media
哈勃极深场
Credit: NASA, ESA, and S. Beckwith (STScI) and HUDF Team credit link
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
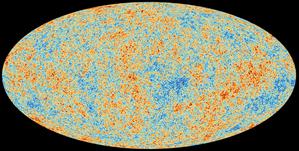
宇宙微波背景辐射
Credit: 欧空局/普朗克合作组织 credit link
License: CC-BY-SA-4.0 Creative Commons 署名-相同方式共享 4.0 国际 (CC BY-SA 4.0) icons