Glossary term: 視差
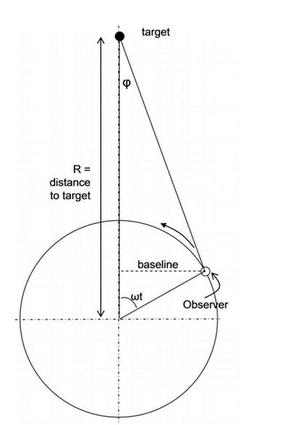
Description: 視差是由於觀察者視點的變化,導致天體在天空中位置的表觀變化。天空中的位置變化,以角度表示,是相對於我們所知道的最遠的物體來確定的——過去是使用遙遠的恆星;是被稱為類星體的極其遙遠的物體,它們確定了所謂的國際天球參考框架。視位置變化的角度與天體離我們的距離成反比,因此視差測量是確定鄰域天體距離的有力工具("視差法")。對於太陽系天體,從地球上不同位置同時進行觀測可以得到有效的視差值。對於恆星來說,視差角是觀測者位置與視線成直角移動一個天文單位(地球-太陽平均距離)時的偏移值。觀測者的位置移動量可以通過相隔幾個月的觀測來實現,在這幾個月之間,地球沿著圍繞太陽的軌道移動。根據定義,在這種條件下視差角為 1 弧秒的天體與地球的距離為 1 秒差距(3.26 光年)。在一年中,恆星在天空中的視位置會劃出一個橢圓,其半主軸就是視差角。迄今為止最精確的恆星視差是由歐空局的蓋亞任務提供的,蓋亞任務是專門為這項任務設計的太空望遠鏡。
Related Terms:
See this term in other languages
Term and definition status: The original definition of this term in English have been approved by a research astronomer and a teacher The translation of this term and its definition is still awaiting approval
This is an automated transliteration of the simplified Chinese translation of this term
The OAE Multilingual Glossary is a project of the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education (OAE) in collaboration with the IAU Office of Astronomy Outreach (OAO). The terms and definitions were chosen, written and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits here. All glossary terms and their definitions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE".
If you notice a factual or translation error in this glossary term or definition then please get in touch.
Related Activities
The 4-Point Backyard Diurnal Parallax Method
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Measure the distance to an asteroid with a novel technique
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 姓名標示 4.0 國際 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Hands-on
, Measurement
, Distances
, CCD imaging
, astrometry
Age Ranges:
16-19
, 19+
Education Level:
Informal
, Secondary
, University
Areas of Learning:
Guided-discovery learning
, Project-based learning
Costs:
High Cost
Duration:
several days
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Analysing and interpreting data
, Asking questions
, Communicating information
, Constructing explanations
, Planning and carrying out investigations
, Using mathematics and computational thinking