Glossary term: 黃道
Description: 黃道是地球繞太陽運行的軌道平面投影到天球上所形成的天球大圓。實際上,黃道是一年中太陽在恆星間劃過的軌跡。所有黃道星座都位於黃道沿線,從地球上觀測到的八大行星也相對靠近黃道。
Related Terms:
See this term in other languages
Term and definition status: The original definition of this term in English have been approved by a research astronomer and a teacher The translation of this term and its definition is still awaiting approval
This is an automated transliteration of the simplified Chinese translation of this term
The OAE Multilingual Glossary is a project of the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education (OAE) in collaboration with the IAU Office of Astronomy Outreach (OAO). The terms and definitions were chosen, written and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits here. All glossary terms and their definitions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE".
If you notice a factual or translation error in this glossary term or definition then please get in touch.
Related Diagrams
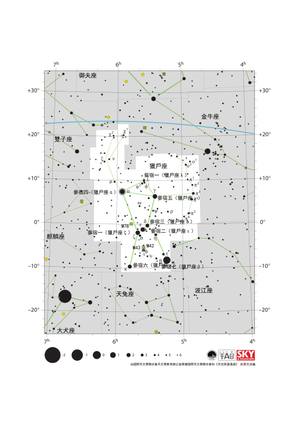
獵戶座星圖
Credit: 由國際天文學聯合會天文教育辦公室根據國際天文學聯合會/《天空與望遠鏡》的原文改編
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 姓名標示 4.0 國際 (CC BY 4.0) icons
天秤座星圖
Credit: 國際天文學聯合會天文教育辦公室(IAU OAE)根據國際天文學聯合會和《天空與望遠鏡》的原文改編
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 姓名標示 4.0 國際 (CC BY 4.0) icons
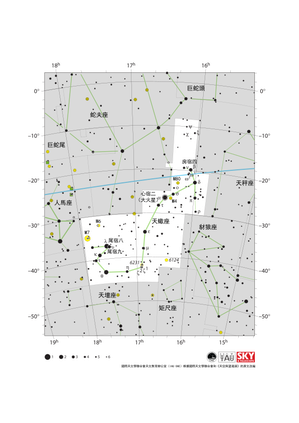
天蠍座星圖
Credit: 國際天文學聯合會天文教育辦公室(IAU OAE)根據國際天文學聯合會和《天空與望遠鏡》的原文改編
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 姓名標示 4.0 國際 (CC BY 4.0) icons
人馬座星圖
Credit: 國際天文學聯合會天文教育辦公室(IAU OAE)根據國際天文學聯合會和《天空與望遠鏡》的原文改編
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 姓名標示 4.0 國際 (CC BY 4.0) icons
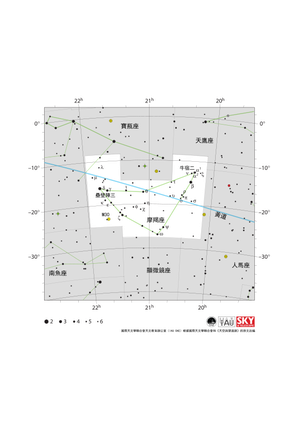
摩羯座星圖
Credit: 國際天文學聯合會天文教育辦公室(IAU OAE)根據國際天文學聯合會和《天空與望遠鏡》的原文改編
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 姓名標示 4.0 國際 (CC BY 4.0) icons