Loading...
Related Media
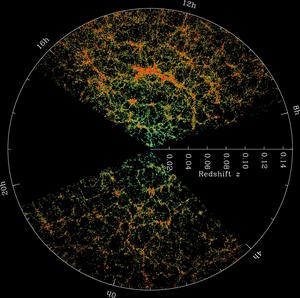
SDSS Redshift Map
Caption: This image shows a map of the distribution of galaxies and is based on redshift data from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS). Redshift measurements provides information on the distances, positions and motions of the galaxies.
The Earth is located at the center of the image, and each dot represents a galaxy. The outer circle represents a ""distance"" of about 2 billion light years. The idea of distance in cosmology is complex because the usual measurement of distance is the separation between two points in space at the same time. However, because of the speed of light, the further a distance, the farther back in time we are observing. The numbers on the outer circle are Right Ascension coordinates mapped onto a flat circle, and provides information on the position of the galaxies on the sky. The colours used represent the ages of the stars in the galaxies, the redder, more strongly clustered points represent galaxies comprising of older stars. The dark wedges that do not contain any dots are regions that were not mapped by the SDSS due to dust from the Milky Way galaxy obscuring the view.
Credit: M. Blanton and Sloan Digital Sky Survey credit link
Credit: M. Blanton and Sloan Digital Sky Survey credit link
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons نَسب المُصنَّف 4.0 دولي (CC BY 4.0) icons