Glossary term: Apparent Magnitude
Description: Apparent magnitude is a measure of how bright a celestial body appears to an observer. For historical reasons, the magnitude scale assigns larger numbers to fainter objects. Magnitude is a logarithmic scale with a difference of five magnitudes corresponding to a factor of 100 in measured brightness. There are many magnitude scales because brightness can be measured at different wavelengths and with different techniques. The common "visual magnitude" scale is set so that the bright star Vega has an apparent magnitude of zero. On this scale, Sirius, the brightest star in the night sky, has magnitude -1.46, and the magnitudes of the Sun and the full Moon are -26.7 and -12.7, respectively. The negative numbers indicate that these objects appear brighter than Vega. In very dark conditions, people with excellent vision can see stars up to about visual magnitude 6. The Hubble Ultra Deep Field reaches a visual magnitude near 31. This is about 100 to the power five or 10,000,000,000 times fainter than magnitude 6.
Related Terms:
See this term in other languages
Term and definition status: This term and its definition have been approved by a research astronomer and a teacher
The OAE Multilingual Glossary is a project of the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education (OAE) in collaboration with the IAU Office of Astronomy Outreach (OAO). The terms and definitions were chosen, written and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits here. All glossary terms and their definitions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE".
If you notice a factual error in this glossary definition then please get in touch.
Related Diagrams
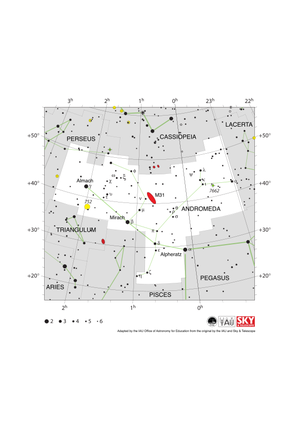
Andromeda Constellation Map
Credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by IAU/Sky & Telescope
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
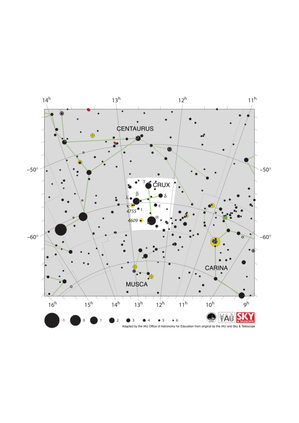
Crux Constellation Map
Credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by IAU/Sky & Telescope.
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
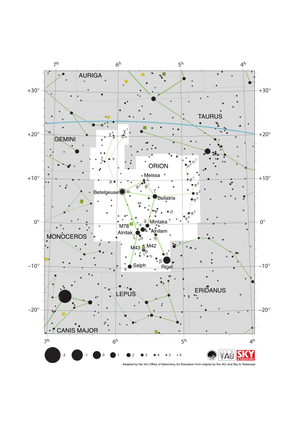
Orion Constellation Map
Credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by IAU/Sky & Telescope
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Libra Constellation Map
Credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by IAU/Sky & Telescope
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
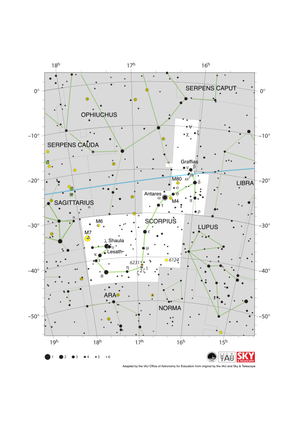
Scorpius Constellation Map
Credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by IAU/Sky & Telescope
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons