Glossary term: Atmosfera
Description: A atmosfera é uma camada de gás que envolve um corpo celeste. Ela é mantida por causa da atração gravitacional do corpo celeste e, portanto, é mais densa na superfície e se funde com o espaço interplanetário em grandes altitudes.
Para planetas com superfícies sólidas ou líquidas, o limite inferior da atmosfera é definido. As estrelas têm interiores gasosos e, portanto, não têm um limite inferior claro para suas atmosferas. Uma atmosfera estelar normalmente se refere à camada gasosa externa de uma estrela através da qual a luz do interior viaja para o espaço.
O campo magnético de um planeta pode proteger sua atmosfera de se dissipar rapidamente no espaço devido ao vento solar ou estelar. No caso da Terra, ele também protege todos os organismos contra danos genéticos devido aos efeitos nocivos do vento solar e dos raios cósmicos.
Related Terms:
See this term in other languages
Term and definition status: The original definition of this term in English have been approved by a research astronomer and a teacher The translation of this term and its definition is still awaiting approval
The OAE Multilingual Glossary is a project of the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education (OAE) in collaboration with the IAU Office of Astronomy Outreach (OAO). The terms and definitions were chosen, written and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits here. All glossary terms and their definitions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE".
If you notice a factual or translation error in this glossary term or definition then please get in touch.
Related Activities
Blue Marble in Empty Space
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Students are taken on a virtual journey to outer space to experience that we live on a tiny planet that floats in a vast and empty space.
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Life
, Hands-on
, Model
, Scales
, Distances
, ISS
Age Ranges:
6-8
, 8-10
Education Level:
Primary
, Secondary
Areas of Learning:
Interactive Lecture
, Modelling
Costs:
Low Cost
Duration:
30 mins
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Asking questions
, Communicating information
, Developing and using models
Fizzy Balloons – CO2 in School
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Investigate the properties of carbon dioxide with this fun demonstration.
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Life
, Hands-on
, Chemistry
, Earth Science
, Carbon Dioxide
Age Ranges:
8-10
, 10-12
Education Level:
Primary
, Secondary
Areas of Learning:
Interactive Lecture
, Traditional Science Experiment
Costs:
Medium Cost
Duration:
2 hours
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Analysing and interpreting data
, Asking questions
, Constructing explanations
, Engaging in argument from evidence
, Planning and carrying out investigations
Investigating the Atmosphere – Air Takes Up Space
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Air takes up space even though you cannot see it.
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Geography
, Mathematics
, Air
Age Ranges:
6-8
, 8-10
Education Level:
Primary
Areas of Learning:
Modelling
, Social Research
Costs:
Low Cost
Duration:
1 hour
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Analysing and interpreting data
, Asking questions
, Communicating information
, Constructing explanations
, Planning and carrying out investigations
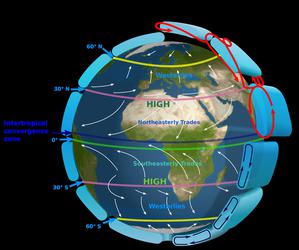
The Intertropical Convergence Zone
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: The air circulation system: how are winds created?
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Climate
, Updraft
, Convection
, Winds
Age Ranges:
12-14
, 14-16
Education Level:
Middle School
Areas of Learning:
Discussion Groups
, Modelling
, Social Research
Costs:
Medium Cost
Duration:
1 hour
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Communicating information
, Constructing explanations
, Developing and using models
, Engaging in argument from evidence
, Planning and carrying out investigations