Glossary term: Câncer
Description: Câncer é uma das constelações do Zodíaco, ou seja, as estrelas que compõem essa constelação estão na parte do céu cruzada pela eclíptica (o plano definido pelo caminho da Terra ao redor do Sol). Portanto, da Terra, podemos encontrar regularmente o Sol e também os planetas na constelação de Câncer. No caso do Sol, isso ocorre no final de julho e início de agosto (nessa época, é claro, não podemos ver as estrelas da constelação). Há dois mil anos, o Sol estava em Câncer durante o solstício de verão do hemisfério norte; essa é a origem do nome Trópico de Câncer. Devido à precessão dos equinócios, o Sol não está mais em Câncer no solstício de verão do hemisfério norte. Câncer é uma das 88 constelações modernas definidas pela União Astronômica Internacional, mas é muito mais antiga — já era uma das 48 constelações nomeadas pelo astrônomo do século II, Cláudio Ptolomeu.
Related Terms:
See this term in other languages
Term and definition status: The original definition of this term in English have been approved by a research astronomer and a teacher The translation of this term and its definition is still awaiting approval
The OAE Multilingual Glossary is a project of the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education (OAE) in collaboration with the IAU Office of Astronomy Outreach (OAO). The terms and definitions were chosen, written and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits here. All glossary terms and their definitions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE".
If you notice a factual or translation error in this glossary term or definition then please get in touch.
Related Media
Most Brightest Stars of the Sky
Credit: Giorgia Hofer/IAU OAE
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Related Diagrams
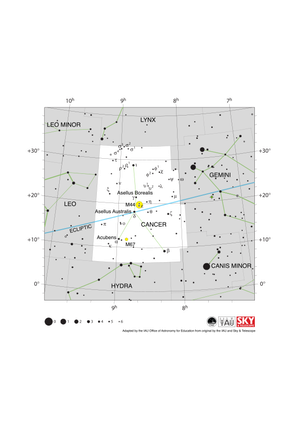
Cancer Constellation Map
Credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by IAU/Sky & Telescope
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
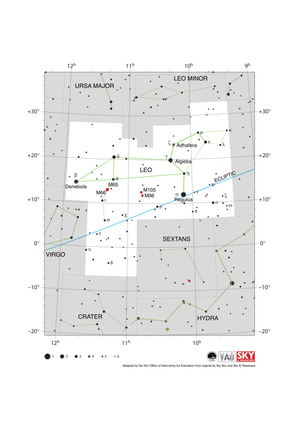
Leo Constellation Map
Credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by IAU/Sky & Telescope
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
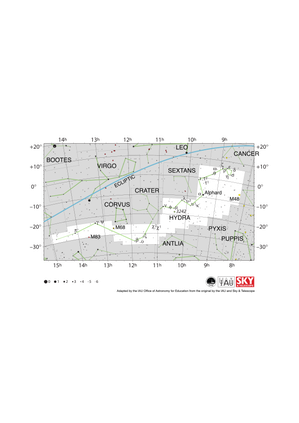
Hydra Constellation Map
Credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by the IAU and Sky & Telescope
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
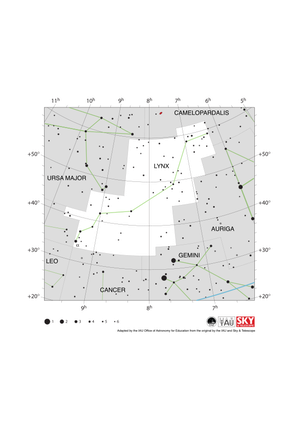
Lynx Constellation Map
Credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by the IAU and Sky & Telescope
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons