Glossary term: Aries
Description: Aries is the smallest constellation in the Zodiac. The stars that make up this constellation are in the part of the sky that intersects with the ecliptic (the plane defined by the orbit of the Earth around the Sun). Hence, from Earth, we can regularly find the planets, and also the Sun, in the constellation Aries. In the case of the Sun this occurs from mid-April to mid-May (at that time, of course, we cannot see the constellation's stars). Aries is one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union, but goes back much further – it was already one of the 48 constellations named by the 2nd century astronomer Claudius Ptolemy.
Related Terms:
See this term in other languages
Term and definition status: This term and its definition have been approved by a research astronomer and a teacher
The OAE Multilingual Glossary is a project of the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education (OAE) in collaboration with the IAU Office of Astronomy Outreach (OAO). The terms and definitions were chosen, written and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits here. All glossary terms and their definitions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE".
If you notice a factual error in this glossary definition then please get in touch.
Related Media
Chilean observatories at home office, by Robert Barsa, Slovakia
Credit: Robert Barsa/IAU OAE
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Related Diagrams
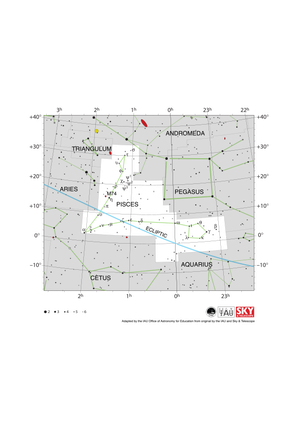
Pisces Constellation Map
Credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by IAU/Sky & Telescope
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
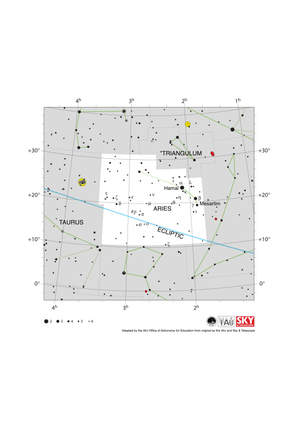
Aries Constellation Map
Credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by IAU/Sky & Telescope
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
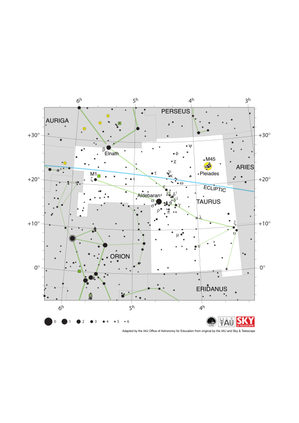
Taurus Constellation Map
Credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by IAU/Sky & Telescope
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Triangulum Constellation Map
Credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by the IAU and Sky & Telescope
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons