Glossary term: 赤经(RA)
Description: 赤经是赤道坐标系中的两个坐标之一(另一个是赤纬),天文学家用以定义天体在天空中的位置。从地球看去,天空中的所有不同位置共同构成了一个以地球为中心的遥远球面,称为天球。天空中地球赤道正上方的点构成了天球上的天赤道,地理北极正上方的点就是北天极,而地理南极正上方的点就是南天极。就像地理学家在地球表面定义地理经纬度一样,天文学家也可以在天球上定义经纬度。但如果我们将天体的经度坐标选择为其正下方的点在地球表面上对应的地理经度值,那么恒星的坐标值就会随着地球的自转而改变。为避免这一点,赤道坐标系的赤经是相对于一条不随地球自转改变,而相对于恒星固定不变的“子午线”来测量的。这条子午线的地位与地球上的格林尼治子午线类似。这条子午线与天赤道的交点定义为太阳从南天球运动到北半球的视轨迹与天赤道相交的确切位置。由此定义的经度称为赤经,其数值自西向东增加。如果在地球上向天赤道看去,则随着地球的自转,所有的赤经值都会在约24小时内依次飞掠而过。因此,赤经通常用时间值来表示,用24小时来代替圆周的360度。赤纬是第二个赤道坐标,与地理纬度相对应。地球自转轴的轻微摆动被称为岁差,它使赤道坐标系——恒星和其他天体的赤经和赤纬——随时间发生变化,但这种变化是非常轻微缓慢的。
Related Terms:
See this term in other languages
Term and definition status: The original definition of this term in English have been approved by a research astronomer and a teacher The translation of this term and its definition is still awaiting approval
The OAE Multilingual Glossary is a project of the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education (OAE) in collaboration with the IAU Office of Astronomy Outreach (OAO). The terms and definitions were chosen, written and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits here. All glossary terms and their definitions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE".
If you notice a factual or translation error in this glossary term or definition then please get in touch.
Related Diagrams
Andromeda Constellation Map
Credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by IAU/Sky & Telescope
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
Crux Constellation Map
Credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by IAU/Sky & Telescope.
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
猎户座星图
Credit: 由国际天文学联合会天文教育办公室根据国际天文学联合会/《天空与望远镜》的原文改编
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
天秤座星图
Credit: 国际天文学联合会天文教育办公室(IAU OAE)根据国际天文学联合会和《天空与望远镜》的原文改编
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
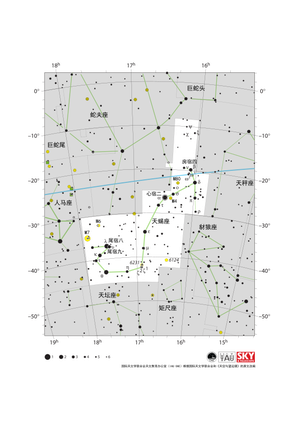
天蝎座星图
Credit: 国际天文学联合会天文教育办公室(IAU OAE)根据国际天文学联合会和《天空与望远镜》的原文改编
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons