Glossary term: 自适应光学
Description: 夜晚抬头仰望,你可能会看到恒星在闪烁。大气中的空气总是在运动,当恒星发出的光经过有湍流的区域时,会发生不同程度的偏转。因此,我们在天空中看到的每颗恒星并不是稳定的单个光点,而是跳跃、不断变化、扭曲的一连串光点。这样的闪烁使得天文学家无法以大型地面望远镜本应达到的水平拍摄到天体的详细图像。自适应光学是减轻这种效应的一种方法。自适应光学(AO)系统利用真实的恒星或是激光投射的“人造恒星”,实时监测大气畸变。进入望远镜的光线被引导到一面可变形的镜子上。在计算机的控制下,镜面以适当的方式不断变形,以抵消大气畸变的影响。
Related Terms:
See this term in other languages
Term and definition status: The original definition of this term in English have been approved by a research astronomer and a teacher The translation of this term and its definition is still awaiting approval
The OAE Multilingual Glossary is a project of the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education (OAE) in collaboration with the IAU Office of Astronomy Outreach (OAO). The terms and definitions were chosen, written and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits here. All glossary terms and their definitions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE".
If you notice a factual or translation error in this glossary term or definition then please get in touch.
Related Media
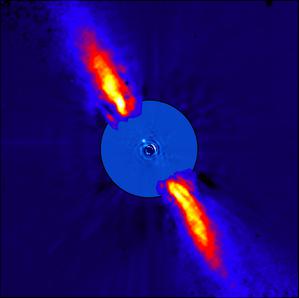
老人增四b
Credit: ESO/A.-M. Lagrange et al. credit link
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons
位于帕拉纳尔天文台的欧洲南方天文台甚大望远镜与月晕
Credit: 胡安-卡洛斯-穆尼奥斯-马特奥斯/欧空局 credit link
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons