Glossary term: G 型星
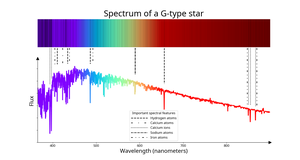
Description: 光谱类型为"G"的恒星。天文学家通过识别电离钙的强吸收线来确定G型恒星;更广泛地说,G型恒星中的金属吸收线比更热的恒星(如F型恒星)更强,而比更冷的恒星(如K型恒星)更弱。G型恒星的典型(有效)温度在5200开尔文(K)到6000 K之间。与其他恒星相比,它们对人类肉眼呈现出黄色,除非存在显著的星际或大气层红化现象。处于主序阶段的G型恒星,即通过核聚变在核心区域将氢转化为氦的恒星,被称为黄矮星。太阳就是一个典型的G型黄矮星例子。
Related Terms:
See this term in other languages
Term and definition status: The original definition of this term in English have been approved by a research astronomer and a teacher The translation of this term and its definition is still awaiting approval
The OAE Multilingual Glossary is a project of the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education (OAE) in collaboration with the IAU Office of Astronomy Outreach (OAO). The terms and definitions were chosen, written and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits here. All glossary terms and their definitions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE".
If you notice a factual or translation error in this glossary term or definition then please get in touch.
Related Diagrams
Spectrum of a G-type star
Credit: IAU OAE/SDSS/Niall Deacon
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0) icons