Glossary term: O-type Star
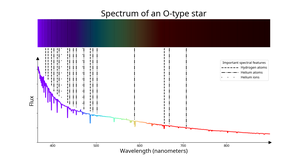
Description: A star with spectral type "O". Astronomers identify O-type stars by the presence of absorption lines from ionized helium in their spectra. They have typical (effective) temperatures greater than around 30,000 kelvins (K). Compared to other stars, they appear bluish-white to human eyes unless interstellar or atmospheric reddening is important. O-type stars are the hottest and bluest of the main spectral classifications. O-type stars on the main sequence have the highest masses (greater than about 15 solar masses), shortest hydrogen burning lifetimes, and, as a result, are mostly found in and around star-forming regions.
Related Terms:
- Hydrogen Fusion
- Main Sequence
- Spectral Type
- Star Formation
- Reddening
- Effective Temperature
- Absorption Line
See this term in other languages
Term and definition status: This term and its definition is still awaiting approval
The OAE Multilingual Glossary is a project of the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education (OAE) in collaboration with the IAU Office of Astronomy Outreach (OAO). The terms and definitions were chosen, written and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits here. All glossary terms and their definitions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE".
Related Diagrams
Spectrum of an O-type star
Credit: IAU OAE/SDSS/Niall Deacon
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons