Glossary term: Venus
Description: Venus is the second closest planet to the Sun. Often called the Earth's twin it is a rocky, terrestrial planet with a radius a little greater than 6000 kilometers (km), about 95% of the Earth's radius. It has a mass of 0.815 times the mass of the Earth. The atmosphere of Venus is 90 times denser than Earth’s. It is mainly composed of carbon dioxide, together with thick clouds of sulfuric acid that shroud the entire surface. The thick atmosphere produces a very strong greenhouse effect, which results in a surface temperature of 460 degrees Celsius.
Its typical distance from the Sun is 108 million kilometers, about 0.72 astronomical units (Earth–Sun distances). It takes 224.7 days to complete one orbit. Venus takes a long time to rotate once along its axis with respect to the distant stars; one such Venus day corresponds to 243 Earth days. This is longer than the time it takes Venus to complete one orbit around the Sun. Venus has no known moons.
Venus is named after the Roman goddess of love. Since Venus is so close to the Sun, it is often visible in the night sky shortly before sunrise or after sunset. On these occasions, Venus is conspicuously bright even when seen with the naked eye, and is traditionally referred to as the morning star or evening star, respectively. With binoculars, Venus can be seen to have phases similar to those of the Moon.
Related Terms:
See this term in other languages
Term and definition status: This term and its definition have been approved by a research astronomer and a teacher
The OAE Multilingual Glossary is a project of the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education (OAE) in collaboration with the IAU Office of Astronomy Outreach (OAO). The terms and definitions were chosen, written and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits here. All glossary terms and their definitions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE".
If you notice a factual error in this glossary definition then please get in touch.
Related Media
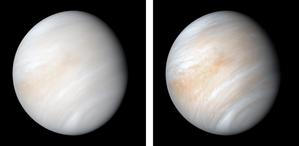
Venus in visible light
Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech credit link
License: PD Public Domain icons
Venus' surface
Credit: NASA/JPL credit link
License: PD Public Domain icons
To guard the Stars and the Sea Together
Credit: Likai Lin/IAU OAE
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Romanian Orion
Credit: Alex Conu/IAU OAE
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
A Matter of Perspective
Credit: Christofer Baez/IAU OAE (CC BY 4.0)
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Related Activities
Children's Planetary Maps: Venus
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Learn more about our nearest neighbour
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags:
Planetary cartography
, Spatial thinking
Age Ranges:
6-8
, 8-10
, 10-12
, 12-14
Education Level:
Middle School
, Primary
, Secondary
Areas of Learning:
Social Research
Costs:
Low Cost
Duration:
2 hours
Group Size:
Group
Skills:
Analysing and interpreting data
, Asking questions
, Communicating information
, Constructing explanations
, Developing and using models
, Engaging in argument from evidence
, Planning and carrying out investigations