This page describes an image Lyra Constellation Map
Download PDF File (PDF file 160.41 kB)
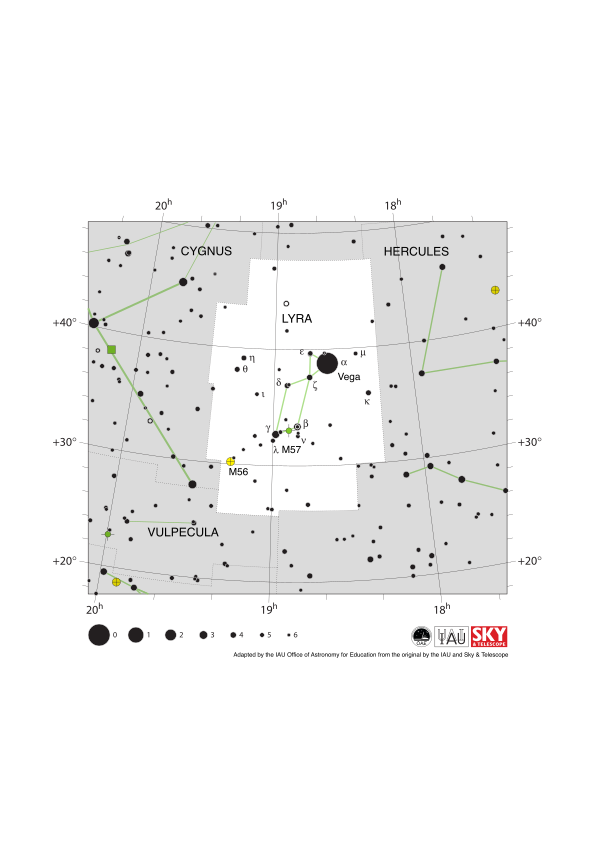
Diagram caption:
The constellation Lyra with its bright stars and surrounding constellations. Lyra is surrounded by (going clockwise from the top): Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula and Cygnus. Lyra is dominated by its brightest star Vega which is used to define the zero point of one of the most commonly used magnitude scales of stellar brightness. Vega forms one vertex of the prominent Summer Triangle asterism that is visible in northern hemisphere summer evenings.
Lyra is a northern constellation and thus is visible at some point in the year throughout the northern hemisphere. The whole constellation is also visible from all equatorial and some temperate regions of the southern hemisphere. Parts of the constellation are visible from the remaining southern temperate areas. Lyra is best viewed in the evenings in the northern hemisphere summer and southern hemisphere winter.
The famous planetary nebula M57, commonly known as the Ring Nebula, lies in Lyra. It is marked here with a green circle superimposed on a plus sign. The globular cluster M56 also lies in Lyra and is marked here with a yellow circle with a plus sign superimposed on it.
The y-axis of this diagram is in degrees of declination with north as up and the x-axis is in hours of right ascension with east to the left. The sizes of the stars marked here relate to the star's apparent magnitude, a measure of its apparent brightness. The larger dots represent brighter stars. The Greek letters mark the brightest stars in the constellation. These are ranked by brightness with the brightest star being labeled alpha, the second brightest beta, etc., although this ordering is not always followed exactly. The dotted boundary lines mark the IAU's boundaries of the constellations and the solid green lines mark one of the common forms used to represent the figures of the constellations. Neither the constellation boundaries, nor the lines joining the stars appear on the sky.
Diagram credit: Adapted by the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education from the original by the IAU and Sky & Telescope. Credit Link
Related glossary terms:
Apparent Magnitude
, Asterism
, Celestial Coordinates
, Constellation
, Declination
, Globular Cluster
, Planetary Nebula
, Right Ascension (RA)
Categories:
Naked Eye Astronomy
Diagram license: Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
The diagram captions presented on the OAE website were written, translated and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits for our translation project here. All media file captions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE". The media files themselves may have different licenses (see above) and should be credited as listed above under "credit".
If you notice a error in this diagram or its caption then please get in touch.