Glossary term: K-type Star
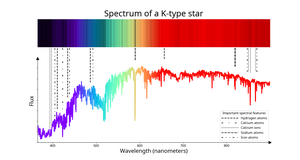
Description: A star with spectral type "K". Astronomers identify K-type stars by the presence of very weak hydrogen lines but strong lines from iron and manganese atoms in their spectra. They have typical (effective) temperatures between around 3700 kelvins (K) and 5200 K. Compared to other stars, they appear orange-white to human eyes unless interstellar or atmospheric reddening is important. Examples of K-type stars are Aldebaran, in Taurus, and Pollux, in Gemini.
Related Terms:
See this term in other languages
Term and definition status: This term and its definition have been approved by a research astronomer and a teacher
The OAE Multilingual Glossary is a project of the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education (OAE) in collaboration with the IAU Office of Astronomy Outreach (OAO). The terms and definitions were chosen, written and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits here. All glossary terms and their definitions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE".
If you notice a factual error in this glossary definition then please get in touch.
Related Diagrams
Spectrum of a K-type star
Credit: IAU OAE/SDSS/Niall Deacon
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons