Glossary term: Redshift
Description: This term can refer to three different effects: Doppler, cosmological, or gravitational redshift. Doppler redshift is the opposite of blueshift; in the case of redshift, the source emitting the electromagnetic radiation is moving away from the observer, and so the wavelength of the electromagnetic radiation is stretched to longer (redder) wavelengths. This is similar to the Doppler effect in the context of sound waves. Cosmological redshift is the result of electromagnetic radiation emitted by a source being stretched to longer wavelengths because of the physical expansion of space, unlike Doppler redshift which is due to relative motion. Gravitational redshift refers to the effect where the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation emitted from a source is stretched to longer wavelengths, or rather the associated photons lose energy as they try to leave a region (gravitational well) where the gravity is stronger.
Related Terms:
See this term in other languages
Term and definition status: This term and its definition have been approved by a research astronomer and a teacher
The OAE Multilingual Glossary is a project of the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education (OAE) in collaboration with the IAU Office of Astronomy Outreach (OAO). The terms and definitions were chosen, written and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits here. All glossary terms and their definitions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE".
If you notice a factual error in this glossary definition then please get in touch.
Related Media
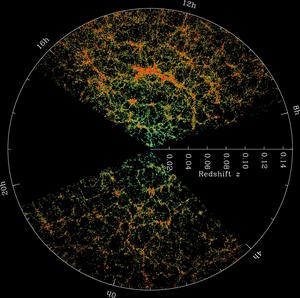
SDSS Redshift Map
Credit: M. Blanton and Sloan Digital Sky Survey credit link
License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons