Glossary term: Saisons
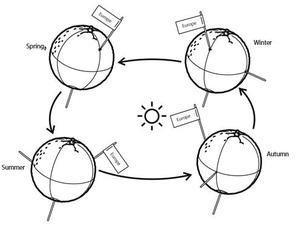
Description: L'axe de la Terre n'est pas perpendiculaire à l'orbite terrestre autour du Soleil, mais incliné d'un angle de 23,4 degrés. Par conséquent, la position apparente du soleil dans le ciel à un moment donné de la journée varie au cours de l'année. Chaque fois que le soleil est, en moyenne, plus haut dans le ciel, une quantité plus importante de lumière du soleil atteint une surface donnée. Au cours de l'année, il en résulte des périodes plus chaudes et plus froides, avec des écarts plus prononcés dans les régions éloignées de l'équateur terrestre, que l'on appelle les saisons. Les saisons de l'hémisphère nord sont opposées à celles de l'hémisphère sud : L'été septentrional, les trois mois centrés sur le 21 juin lorsque l'hémisphère nord est incliné au maximum vers le Soleil, est l'hiver méridional, l'hémisphère sud étant incliné vers l'extérieur, et vice versa pour l'été méridional, qui correspond à la période de trois mois autour du 21 décembre. De nombreuses régions de la Terre proches de l'équateur ont des saisons qui diffèrent du schéma été-hiver observé aux latitudes tempérées et arctiques. Il convient de noter que la durée, le début et la fin de chaque saison peuvent être influencés par les pratiques culturelles et l'époque.
Related Terms:
See this term in other languages
Term and definition status: The original definition of this term in English have been approved by a research astronomer and a teacher The translation of this term and its definition is still awaiting approval
The OAE Multilingual Glossary is a project of the IAU Office of Astronomy for Education (OAE) in collaboration with the IAU Office of Astronomy Outreach (OAO). The terms and definitions were chosen, written and reviewed by a collective effort from the OAE, the OAE Centers and Nodes, the OAE National Astronomy Education Coordinators (NAECs) and other volunteers. You can find a full list of credits here. All glossary terms and their definitions are released under a Creative Commons CC BY-4.0 license and should be credited to "IAU OAE".
Related Activities
Sun’s Shadow
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Why is the Sun's shadow so important?License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags: Hands-on , Shadows Age Ranges: 6-8 , 8-10 , 10-12 , 12-14 , 14-16 Education Level: Informal , Middle School , Primary , Secondary Areas of Learning: Observation based , Social Research Costs: Medium Cost Duration: 1 day Group Size: Group Skills: Asking questions , Communicating information , Constructing explanations , Engaging in argument from evidenceSeasons Around the World
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Demonstrate the seasons on Earth using a model.License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags: Hands-on , Model Age Ranges: 6-8 , 8-10 , 10-12 Education Level: Middle School , Primary Areas of Learning: Modelling , Social Research Costs: Medium Cost Duration: 45 mins Group Size: Group Skills: Analysing and interpreting data , Asking questions , Constructing explanations , Developing and using models , Planning and carrying out investigationsNavigate like a Viking – Use the Sun, not your phone!
astroEDU educational activity (links to astroEDU website) Description: Learn how the Vikings used the sky to navigate at sea with a hands-on activity!License: CC-BY-4.0 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) icons
Tags: History , Geography , Maps , Coordinates , Celestial navigation Age Ranges: 12-14 , 14-16 Education Level: Middle School Areas of Learning: Discussion Groups , Modelling , Social Research Costs: Medium Cost Duration: 1 hour 30 mins Group Size: Group Skills: Analysing and interpreting data , Asking questions , Communicating information , Developing and using models , Planning and carrying out investigations , Using mathematics and computational thinking